Difference between revisions of "Time of bloom"
From GcatWiki
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
Ambient Temperature Pathway | Ambient Temperature Pathway | ||
*Unlike "the photoperiod and vernalisation pathways [which] monitor seasonal changes in day length or temperature and ... [respond] to exposure to long days or prolonged cold temperatures, the ambient temperature pathway coordinates the response to daily growth temperatures" ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) | *Unlike "the photoperiod and vernalisation pathways [which] monitor seasonal changes in day length or temperature and ... [respond] to exposure to long days or prolonged cold temperatures, the ambient temperature pathway coordinates the response to daily growth temperatures" ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) | ||
| − | *16 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the ambient temperature pathway: AGL31, ATARP6, ATBZIP27, FCA, FD, FLC, FLD, FT, FVE, MAF1, MAF3, MAF4, MAF5, SVP, TFL1, TSF | + | *16 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the ambient temperature pathway: AGL31, ATARP6, ATBZIP27, FCA, FD, FLC, FLD, FT, FVE, MAF1, MAF3, MAF4, MAF5, SVP, TFL1, TSF ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) |
Autonomous Pathway | Autonomous Pathway | ||
*The autonomous pathway is "activated in response to endogenous changes that are independent from the environmental cues leading to flowering", such as the plant's circadian rhythm ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) | *The autonomous pathway is "activated in response to endogenous changes that are independent from the environmental cues leading to flowering", such as the plant's circadian rhythm ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) | ||
| − | *17 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the autonomous pathway: CLF, FCA, FIE1, FLD, FLK, FPA, FVE, FY, LD, MSI1, SWN, VEL1, VEL2, VEL3, VIN3, VRN2, VRN5 | + | *17 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the autonomous pathway: CLF, FCA, FIE1, FLD, FLK, FPA, FVE, FY, LD, MSI1, SWN, VEL1, VEL2, VEL3, VIN3, VRN2, VRN5 ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) |
Light Signaling Pathway | Light Signaling Pathway | ||
*"Light is one of the main environmental regulators of flowering in plants. Plants sense the time of day and season of year by monitoring the light environment through light signalling pathways." Furthermore, the light signalling pathway is comprised of the "photoperiod pathway genes together with photoreceptor genes and circadian clock components" ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) | *"Light is one of the main environmental regulators of flowering in plants. Plants sense the time of day and season of year by monitoring the light environment through light signalling pathways." Furthermore, the light signalling pathway is comprised of the "photoperiod pathway genes together with photoreceptor genes and circadian clock components" ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) | ||
| − | *48 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the light signaling pathway: APRR3, APRR5, APRR9, AT1G26790, AT1G29160, AT2G34140, AT3G21320, AT3G25730, ATCOL4, ATCOL5, CCA1, CDF1, CDF2, CDF3, CDF5, CHE, CIB1, CO, COL1, COL2, COL9, COP1, CRY1, CRY2, ELF3, ELF4, ELF4-L3, FKF1, GI, LHY, LKP2, LUX, PHYA, PHYB, PHYC, PHYD, PHYE, PRR7, RAV1, RFI2, SPA1, SPA2, SPA3, SPA4, TEM1, TEM2, TOC1, ZTL | + | *48 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the light signaling pathway: APRR3, APRR5, APRR9, AT1G26790, AT1G29160, AT2G34140, AT3G21320, AT3G25730, ATCOL4, ATCOL5, CCA1, CDF1, CDF2, CDF3, CDF5, CHE, CIB1, CO, COL1, COL2, COL9, COP1, CRY1, CRY2, ELF3, ELF4, ELF4-L3, FKF1, GI, LHY, LKP2, LUX, PHYA, PHYB, PHYC, PHYD, PHYE, PRR7, RAV1, RFI2, SPA1, SPA2, SPA3, SPA4, TEM1, TEM2, TOC1, ZTL ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) |
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
Vernalization Pathway | Vernalization Pathway | ||
*The vernalization pathway is the response to "prolonged periods of low temperature [that are required] to initiate flowering" ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) | *The vernalization pathway is the response to "prolonged periods of low temperature [that are required] to initiate flowering" ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) | ||
| − | *32 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the vernalisation pathway: AGL14, AGL19, AGL24, AGL31, ATARP6, ATSWC6, CLF, EFS, FES1, FIE1, FLC, FRI, FRL1, FRL2, HUA2, MAF1, MAF3, MAF4, MAF5, MSI1, PAF1, PAF2, PEP, PIE1, SUF4, SVP, SWN, VEL1, VIN3, VRN1, VRN2, VRN5 | + | *32 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the vernalisation pathway: AGL14, AGL19, AGL24, AGL31, ATARP6, ATSWC6, CLF, EFS, FES1, FIE1, FLC, FRI, FRL1, FRL2, HUA2, MAF1, MAF3, MAF4, MAF5, MSI1, PAF1, PAF2, PEP, PIE1, SUF4, SVP, SWN, VEL1, VIN3, VRN1, VRN2, VRN5 ([http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]) |
Revision as of 17:35, 7 March 2013
By Austin Mudd - Spring 2013
Contents
To Do
- Write introduction and procedure sections
- Continue searching for grape orthologs
Introduction to Flowering
The Process of Flowering
- Flowering is the "switch from vegetative growth (the production of stems and leaves) to reproductive growth (the production of flowers)" (Higgins et al., 2010)
- The “shoot apical meristem starts to produce flowers instead of leaves” (Fornara et al., 2010)
- Occurs “when conditions for pollination and seed development are optimal and consequently most plants restrict flowering to a specific time of year” (Higgins et al., 2010)
- ”The genes and molecular mechanisms controlling flowering have been extensively studied in the model dicot Arabidopsis thaliana” (Higgins et al., 2010)
- In Arabidopsis thaliana, “180 genes have been implicated in flowering-time control based on isolation of loss-of-function mutations or analysis of transgenic plants ... Strikingly, several genes act more than once and in several tissues during floral induction” (Fornara et al., 2010)
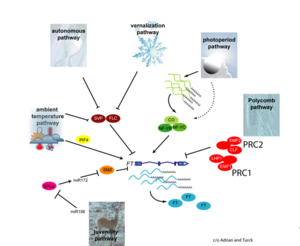
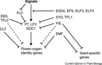
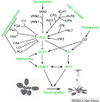
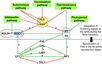
The six major pathways in the timing of flowering from the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research
The Timing of Flowering
- Flowering is controlled by “six major pathways: the photoperiod and vernalization pathways control flowering in response to seasonal changes in day length and temperature; the ambient temperature pathway responds to daily growth temperatures; and the age, autonomous, and gibberellin pathways act more independently of environmental stimuli.” (Fornara et al., 2010)
- These “six pathways converge to regulate a small number of ‘floral integrator genes,’ ... which govern flowering time by merging signals from multiple pathways” (Fornara et al., 2010)
The Importance of Flowering
- ”Flowering is one of the most important agronomic traits influencing crop yield” (Jung et al., 2012)
- ”Flowering time is important for adaptation to specific environments and the world's major crop species provide a particularly interesting opportunity for study because they are grown in areas outside the ecogeographical limits of their wild ancestors” (Higgins et al., 2010)
- “Adaptation to different environments and practices has been achieved by manipulation of flowering time responses” (Higgins et al., 2010)
- The study of flowering is ”critical for the breeding of climate change resilient crop varieties” (Jung et al., 2012)
- Flowering is “an excellent system for comparison between and within domestic and wild species” (Higgins et al., 2010)
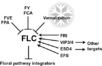
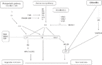
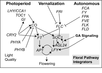
6 Pathways Controlling Flowering
Age / Gibberellin
- "SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING-LIKE (SPL) transcription factors were previously shown to promote flowering and to be repressed by microRNA156 (miR156). The abundance of miR156 is high in young plants and falls as the plant ages, allowing SPL activity to rise in older plants. This paper shows that the activity of one SPL transcription factor, SPL9, is also regulated post-transcriptionally by the growth regulator gibberellin (GA). SPL9 is shown to interact directly with the DELLA protein RGA, which represses SPL9 activity. RGA is known to be degraded in response to GA, which would therefore allow SPL9 to be released from DELLA inactivation. Thus, this paper demonstrates that the promotive effect of SPL9 on floral transition is restrained by two post-transcriptional mechanisms – miR156 and GA levels. This combination is likely to be significant in ensuring that SPL activity is restricted to plants of appropriate age and/or exposed to inductive environmental conditions."
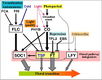
Ambient Temperature Pathway
- Unlike "the photoperiod and vernalisation pathways [which] monitor seasonal changes in day length or temperature and ... [respond] to exposure to long days or prolonged cold temperatures, the ambient temperature pathway coordinates the response to daily growth temperatures" (Jung et al., 2012)
- 16 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the ambient temperature pathway: AGL31, ATARP6, ATBZIP27, FCA, FD, FLC, FLD, FT, FVE, MAF1, MAF3, MAF4, MAF5, SVP, TFL1, TSF (Jung et al., 2012)
Autonomous Pathway
- The autonomous pathway is "activated in response to endogenous changes that are independent from the environmental cues leading to flowering", such as the plant's circadian rhythm (Jung et al., 2012)
- 17 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the autonomous pathway: CLF, FCA, FIE1, FLD, FLK, FPA, FVE, FY, LD, MSI1, SWN, VEL1, VEL2, VEL3, VIN3, VRN2, VRN5 (Jung et al., 2012)
Light Signaling Pathway
- "Light is one of the main environmental regulators of flowering in plants. Plants sense the time of day and season of year by monitoring the light environment through light signalling pathways." Furthermore, the light signalling pathway is comprised of the "photoperiod pathway genes together with photoreceptor genes and circadian clock components" (Jung et al., 2012)
- 48 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the light signaling pathway: APRR3, APRR5, APRR9, AT1G26790, AT1G29160, AT2G34140, AT3G21320, AT3G25730, ATCOL4, ATCOL5, CCA1, CDF1, CDF2, CDF3, CDF5, CHE, CIB1, CO, COL1, COL2, COL9, COP1, CRY1, CRY2, ELF3, ELF4, ELF4-L3, FKF1, GI, LHY, LKP2, LUX, PHYA, PHYB, PHYC, PHYD, PHYE, PRR7, RAV1, RFI2, SPA1, SPA2, SPA3, SPA4, TEM1, TEM2, TOC1, ZTL (Jung et al., 2012)
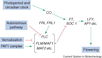
Polycomb Pathway
- "Arabidopsis Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) subunits CURLY LEAF (CLF), EMBRYONIC FLOWER 2 (EMF2) and FERTILIZATION INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM (FIE) repress the expression of FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC), a central repressor of the floral transition in Arabidopsis and FLC relatives ... CLF and FIE strongly repress the expression of FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) ... CLF-containing PRC2-like complexes play a significant role in control of flowering in Arabidopsis."
Vernalization Pathway
- The vernalization pathway is the response to "prolonged periods of low temperature [that are required] to initiate flowering" (Jung et al., 2012)
- 32 Arabidopsis genes are involved in the vernalisation pathway: AGL14, AGL19, AGL24, AGL31, ATARP6, ATSWC6, CLF, EFS, FES1, FIE1, FLC, FRI, FRL1, FRL2, HUA2, MAF1, MAF3, MAF4, MAF5, MSI1, PAF1, PAF2, PEP, PIE1, SUF4, SVP, SWN, VEL1, VIN3, VRN1, VRN2, VRN5 (Jung et al., 2012)
Procedure
- Overall procedure for finding the genes, running with GenSAS, determining SSRs, etc
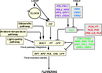
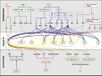
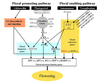
Gallery of Arabidopsis Flowering Pathways
93 Flowering Genes
This table lists 93 genes involved in the ambient temperature, autonomous, light signaling, and vernalization pathways, all of which "have been implicated in flowering-time control based on isolation of loss-of-function mutations or analysis of transgenic plants." (Fornara et al., 2010) All Arabidopsis genes are compiled from Jung et al., 2012. All potential orthologs are found via UniProt Grape nomenclature search.
| Arabidopsis Locus | Other Names | AA Sequence | Pathway | Potential Ortholog |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT1G01060 | LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL, LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 1, LHY, LHY1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G04400 | AT-PHH1, ATCRY2, CRY2, CRYPTOCHROME 2, FHA, PHH1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G09570 | ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 8, FAR RED ELONGATED 1, FAR RED ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 2, FHY2, FRE1, HY8, PHYA, PHYTOCHROME A | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT1G13260 | EDF4, ETHYLENE RESPONSE DNA BINDING FACTOR 4, RAV1, RELATED TO ABI3/VP1 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G20330 | COTYLEDON VASCULAR PATTERN 1, CVP1, FRILL1, FRL1, SMT2, STEROL METHYLTRANSFERASE 2 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT1G22770 | FB, GI, GIGANTEA | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G25560 | EDF1, ETHYLENE RESPONSE DNA BINDING FACTOR 1, TEM1, TEMPRANILLO 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G26790 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT1G29160 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT1G30970 | SUF4, SUPPRESSOR OF FRIGIDA4 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT1G31814 | FRIGIDA LIKE 2, FRL2 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT1G47250 | 20S PROTEASOME ALPHA SUBUNIT F2, PAF2 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT1G53090 | SPA1-RELATED 4, SPA4 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G65480 | FLOWERING LOCUS T, FT | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator | Grape |
| AT1G68050 | "FLAVIN-BINDING, KELCH REPEAT, F BOX 1", ADO3, FKF1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G68840 | ATRAV2, EDF2, ETHYLENE RESPONSE DNA BINDING FACTOR 2, RAP2.8, RAV2, RELATED TO ABI3/VP1 2, RELATED TO AP2 8, TEM2, TEMPRANILLO 2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G77080 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 27, AGL27, FLM, FLOWERING LOCUS M, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 1, MAF1 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | |
| AT1G77300 | ASH1 HOMOLOG 2, ASHH2, CAROTENOID CHLOROPLAST REGULATORY1, CCR1, EARLY FLOWERING IN SHORT DAYS, EFS, LAZ2, LAZARUS 2, SDG8, SET DOMAIN GROUP 8 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT2G06255 | ELF4-L3, ELF4-LIKE 3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G17770 | ATBZIP27, BASIC REGION/LEUCINE ZIPPER MOTIF 27, BZIP27, FD PARALOG, FDP | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Meristem identity | |
| AT2G18790 | HY3, OOP1, OUT OF PHASE 1, PHYB, PHYTOCHROME B | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT2G18870 | VEL3, VERNALIZATION5/VIN3-LIKE 3, VIL4, VIN3-LIKE 4 | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT2G18880 | VEL2, VERNALIZATION5/VIN3-LIKE 2, VIL3, VIN3-LIKE 3 | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT2G18915 | ADAGIO 2, ADO2, LKP2, LOV KELCH PROTEIN 2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G19520 | ACG1, ATMSI4, FVE, MSI4, MULTICOPY SUPPRESSOR OF IRA1 4, NFC04, NFC4 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Autonomous | |
| AT2G22540 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 22, AGL22, SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE, SVP | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Vernalization | Grape |
| AT2G23380 | CLF, CURLY LEAF, ICU1, INCURVATA 1, SDG1, SET1, SETDOMAIN 1, SETDOMAIN GROUP 1 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT2G25930 | EARLY FLOWERING 3, ELF3, PYK20 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G32950 | ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1, ATCOP1, CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1, COP1, DEETIOLATED MUTANT 340, DET340, EMB168, EMBRYO DEFECTIVE 168, FUS1, FUSCA 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G33835 | FES1, FRIGIDA-ESSENTIAL 1 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT2G34140 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT2G40080 | EARLY FLOWERING 4, ELF4 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G43410 | FPA | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT2G46340 | SPA1, SUPPRESSOR OF PHYA-105 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G46790 | APRR9, ARABIDOPSIS PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 9, PRR9, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 9, TL1, TOC1-LIKE PROTEIN 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G46830 | ATCCA1, CCA1, CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G47700 | RED AND FAR-RED INSENSITIVE 2, RFI2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G02380 | ATCOL2, B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 3, BBX3, COL2, CONSTANS-LIKE 2 | TAIR | Flowering integrator, Light signaling | |
| AT3G04610 | FLK, FLOWERING LOCUS KH DOMAIN | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT3G07650 | B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 7, BBX7, COL9, CONSTANS-LIKE 9 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G10390 | FLD, FLOWERING LOCUS D | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Autonomous | |
| AT3G12810 | CHR13, PHOTOPERIOD-INDEPENDENT EARLY FLOWERING 1, PIE1, SRCAP | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT3G15354 | SPA1-RELATED 3, SPA3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G18990 | REDUCED VERNALIZATION RESPONSE 1, REM39, REPRODUCTIVE MERISTEM 39, VRN1 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT3G20740 | FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM, FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM 1, FIE, FIE1, FIS3 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT3G21320 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT3G24440 | VERNALIZATION 5, VIL1, VIN3-LIKE 1, VRN5 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT3G25730 | EDF3, ETHYLENE RESPONSE DNA BINDING FACTOR 3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G33520 | ACTIN-RELATED PROTEIN 6, ARP6, ATARP6, EARLY IN SHORT DAYS 1, ESD1, SUF3, SUPPRESSOR OF FRI 3 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Vernalization | |
| AT3G46640 | LUX, LUX ARRHYTHMO, PCL1, PHYTOCLOCK 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G47500 | CDF3, CYCLING DOF FACTOR 3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT4G00650 | FLA, FLOWERING LOCUS A, FRI, FRIGIDA | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G02020 | EZA1, SDG10, SET DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN 10, SWINGER, SWN | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT4G02560 | LD, LUMINIDEPENDENS | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT4G08920 | ATCRY1, BLU1, BLUE LIGHT UNINHIBITED 1, CRY1, CRYPTOCHROME 1, ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 4, HY4, OOP2, OUT OF PHASE 2 | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT4G11110 | SPA1-RELATED 2, SPA2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT4G11880 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 14, AGL14 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G16250 | PHYD, PHYTOCHROME D | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT4G16280 | FCA | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Autonomous | Grape |
| AT4G16845 | REDUCED VERNALIZATION RESPONSE 2, VRN2 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT4G18130 | PHYE, PHYTOCHROME E | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT4G20370 | TSF, TWIN SISTER OF FT | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator | |
| AT4G22950 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 19, AGL19, GL19 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G24540 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 24, AGL24 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G26000 | PEP, PEPPER | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G30200 | VEL1, VERNALIZATION5/VIN3-LIKE 1, VIL2, VIN3-LIKE 2 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT4G34530 | CIB1, CRYPTOCHROME-INTERACTING BASIC-HELIX-LOOP-HELIX 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT4G35900 | ATBZIP14, FD, FD-1 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Meristem identity | |
| AT5G02810 | APRR7, PRR7, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 7 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G03840 | TERMINAL FLOWER 1, TFL1 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator | Grape |
| AT5G08330 | CCA1 HIKING EXPEDITION, CHE, TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR TCP21, TCP21 | UniProtKB | Light signaling | |
| AT5G10140 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 25, AGL25, FLC, FLF, FLOWERING LOCUS C, FLOWERING LOCUS F | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | Grape |
| AT5G13480 | FY | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT5G15840 | B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 1, BBX1, CO, CONSTANS, FG | TAIR | Flowering integrator, Light signaling | |
| AT5G15850 | ATCOL1, B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 2, BBX2, COL1, CONSTANS-LIKE 1 | TAIR | Flowering integrator, Light signaling | |
| AT5G23150 | ENHANCER OF AG-4 2, HUA2 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT5G24470 | APRR5, PRR5, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 5 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G24930 | ATCOL4, B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 5, BBX5, COL4, CONSTANS-LIKE 4 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G35840 | PHYC, PHYTOCHROME C | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT5G37055 | ATSWC6, SEF, SERRATED LEAVES AND EARLY FLOWERING | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT5G39660 | CDF2, CYCLING DOF FACTOR 2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G42790 | ARS5, ARSENIC TOLERANCE 5, ATPSM30, PAF1, PROTEASOME ALPHA SUBUNIT F1 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT5G57360 | ADAGIO 1, ADO1, FKF1-LIKE PROTEIN 2, FKL2, LKP1, LOV KELCH PROTEIN 1, ZEITLUPE, ZTL | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G57380 | VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3, VIN3 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT5G57660 | ATCOL5, B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 6, BBX6, COL5, CONSTANS-LIKE 5 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G58230 | ARABIDOPSIS MULTICOPY SUPRESSOR OF IRA1, ATMSI1, MATERNAL EFFECT EMBRYO ARREST 70, MEE70, MSI1, MULTICOPY SUPRESSOR OF IRA1 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT5G60100 | APRR3, PRR3, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G61380 | APRR1, ATTOC1, PRR1, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 1, TIMING OF CAB EXPRESSION 1, TOC1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G62430 | CDF1, CYCLING DOF FACTOR 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G65050 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 31, AGL31, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 2, MAF2 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | |
| AT5G65060 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 70, AGL70, FCL3, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 3, MAF3 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | |
| AT5G65070 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 69, AGL69, FCL4, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 4, MAF4 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | |
| AT5G65080 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 68, AGL68, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 5, MAF5 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization |