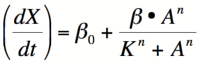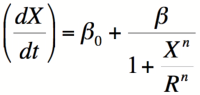|
|
| Line 6: |
Line 6: |
| | | | |
| | ==Modeling Transcription Rates== | | ==Modeling Transcription Rates== |
| − | Note: the following mathematical analysis was developed based on a summary of the input function of a gene in ''An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits'' [[CellularMemory:References |(Alon, pgs 241-250)]]. | + | Note: the following mathematical analysis was developed based on a summary of the input function of a gene in ''An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits'' [[CellularMemory:References |(Alon, pgs. 241-250)]]. |
| | | | |
| | When dealing with gene activation and repression networks, such as those described in the common [[CellularMemory:Biological Designs |Biological Designs]] for synthetic cellular memory section of this paper, one of three mathematical models is often used to model the transcription rate of a gene(s). These three models are, in order of increasing complexity, the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Michaelis-Menten_kinetics Michaelis-Menten] model, the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hill_equation Hill] model, and the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MWC_model Monod-Wymann-Changeux] model. Each model builds on the one preceding it to paint a clearer picture of how binding occurs between two or more molecules. | | When dealing with gene activation and repression networks, such as those described in the common [[CellularMemory:Biological Designs |Biological Designs]] for synthetic cellular memory section of this paper, one of three mathematical models is often used to model the transcription rate of a gene(s). These three models are, in order of increasing complexity, the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Michaelis-Menten_kinetics Michaelis-Menten] model, the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hill_equation Hill] model, and the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MWC_model Monod-Wymann-Changeux] model. Each model builds on the one preceding it to paint a clearer picture of how binding occurs between two or more molecules. |
| Line 22: |
Line 22: |
| | [[Image: Hillrepressor.png|thumb|200px|right|'''Equation 2:'''The Hill equation for a repressor.]] | | [[Image: Hillrepressor.png|thumb|200px|right|'''Equation 2:'''The Hill equation for a repressor.]] |
| | [[Image:linebreak.png]] | | [[Image:linebreak.png]] |
| − |
| |
| | | | |
| | ==Cooperativity== | | ==Cooperativity== |
Revision as of 19:04, 29 November 2007
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Mathematical Models
Mathematical modeling is an important component in the construction of rationally designed gene networks. The complexity of biological systems makes necessary the use of sophisticated mathematical models to accurately predict network functionality. Models are useful in tuning the individual components of a network to increase system robustness. They also provide a basis for comparison of experimental results with expected results, allowing researchers to test the validity of their assumptions.
Modeling Transcription Rates
Note: the following mathematical analysis was developed based on a summary of the input function of a gene in An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits (Alon, pgs. 241-250).
When dealing with gene activation and repression networks, such as those described in the common Biological Designs for synthetic cellular memory section of this paper, one of three mathematical models is often used to model the transcription rate of a gene(s). These three models are, in order of increasing complexity, the Michaelis-Menten model, the Hill model, and the Monod-Wymann-Changeux model. Each model builds on the one preceding it to paint a clearer picture of how binding occurs between two or more molecules.
The Michaelis-Menten Equation
The Hill Equation
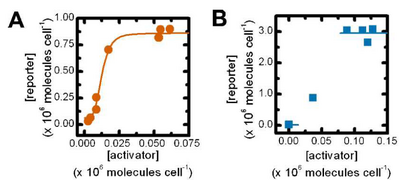
- Three closely related mathematical models can be used to describe binding of two given molecules in a biological system. . All of them can be understood by looking at the definition of the dissociation constant of a given molecular complex. Kd = [A][B]/[AB]. Because [AB] = [Btotal] - [B] you can show that the percentage of unbound B molecules [B]/[Btotal] = 1/(1+X/Kd). If you think of B as a RNA Polymerase binding site and A as a repressor, multiply by the maximal rate of transcription (beta) yields the promoter activity as a function of repressor concentration. (See discussion of Kd below)
- The value of K (the activation/repression coefficient) is closely related to the dissociation constant of the inducer/repressor complex. The dissociation constant measures the propensity for this complex to fall apart. Kd = [I][R]/[IR]. This gives the dissociation constant units of concentration. It can be shown mathematically that Kd is equal to [I] at which half of the repressor is bound to the DNA and half is not ([R] = [IR]). Because the amount of repressor bound to the DNA is proportional to the level of transcription, K (being closely related to Kd) is the value at the inducer yields half of the maximum level of transcription.
- Michaelis-Menton model doesn't take cooperativity into account.
- The Hill equation accounts for cooperativity of binding, but is not a completely accurate description at very low concentrations of repressor/activator.
- The Monod, Changeux, and Wymann model is the most accurate model of these three, but is not commonly used because of its increased complexity and the fact that the hill equation accurately describes most situations.
The Monod-Wymann-Changeux Equation
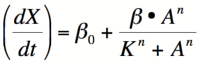 Equation 1: The Hill equation for an activator. 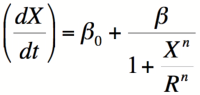 Equation 2:The Hill equation for a repressor. Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Cooperativity
Show how Michaelis-Menton is the same as the hill equation when n=1 and then show what happens as n increases. (graph in book)
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Determining the Values of Funcational Parameters
Put text here.
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Quantitative Part Characterization
Put text here.
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
<Previous Section | Next Section>
|