Difference between revisions of "Time of bloom"
From GcatWiki
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
==105 Flowering Genes== | ==105 Flowering Genes== | ||
| − | This table lists all of the genes involved in the ambient temperature, autonomous, light signaling, and vernalization pathways. All <i>Arabidopsis</i> genes are compiled from [http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]. All potential orthologs are found via [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/?query=taxonomy%3A%22Vitis+vinifera+%28Grape%29+%5B29760%5D%22&sort=score UniProt Grape | + | This table lists all of the genes involved in the ambient temperature, autonomous, light signaling, and vernalization pathways. All <i>Arabidopsis</i> genes are compiled from [http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0038250 Jung et al., 2012]. All potential orthologs are found via [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/?query=taxonomy%3A%22Vitis+vinifera+%28Grape%29+%5B29760%5D%22&sort=score UniProt Grape] nomenclature search. |
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
| AT1G62830||ARABIDOPSIS LYSINE-SPECIFIC HISTONE DEMETHYLASE, ATLSD1, ATSWP1, LDL1, LSD1, LSD1-LIKE 1, LYSINE-SPECIFIC HISTONE DEMETHYLASE, SWP1||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=29274&type=locus TAIR]||Ambient temperature, Autonomous|| | | AT1G62830||ARABIDOPSIS LYSINE-SPECIFIC HISTONE DEMETHYLASE, ATLSD1, ATSWP1, LDL1, LSD1, LSD1-LIKE 1, LYSINE-SPECIFIC HISTONE DEMETHYLASE, SWP1||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=29274&type=locus TAIR]||Ambient temperature, Autonomous|| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | AT1G65480||FLOWERING LOCUS T, FT||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=30541&type=locus TAIR]||Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator||[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/D1MDP3 Grape | + | | AT1G65480||FLOWERING LOCUS T, FT||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=30541&type=locus TAIR]||Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator||[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/D1MDP3 Grape] |
|- | |- | ||
| AT1G68050||"FLAVIN-BINDING, KELCH REPEAT, F BOX 1", ADO3, FKF1||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=137051&type=locus TAIR]||Light signaling|| | | AT1G68050||"FLAVIN-BINDING, KELCH REPEAT, F BOX 1", ADO3, FKF1||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=137051&type=locus TAIR]||Light signaling|| | ||
| Line 264: | Line 264: | ||
| AT5G02810||APRR7, PRR7, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 7||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=131538&type=locus TAIR]||Light signaling|| | | AT5G02810||APRR7, PRR7, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 7||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=131538&type=locus TAIR]||Light signaling|| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | AT5G03840||TERMINAL FLOWER 1, TFL1||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=131459&type=locus TAIR]||Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator||[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q84MI7 Grape | + | | AT5G03840||TERMINAL FLOWER 1, TFL1||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=131459&type=locus TAIR]||Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator||[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q84MI7 Grape] |
|- | |- | ||
| AT5G08230||||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=135669&type=locus TAIR]||Vernalization|| | | AT5G08230||||[http://arabidopsis.org/servlets/TairObject?id=135669&type=locus TAIR]||Vernalization|| | ||
Revision as of 22:36, 6 March 2013
By Austin Mudd - Spring 2013
Contents
To Do
- Write introduction and procedure sections
- Continue searching for grape orthologs
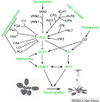
Flowering Introduction
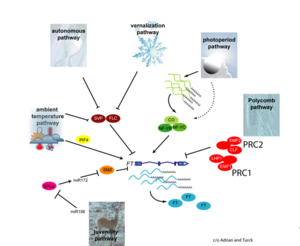
The factors affecting time of flowering from the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research
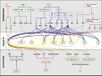
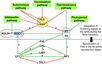
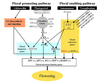
- "Plants initiate flowering after a period of vegetative development. During this process, called floral induction, the shoot apical meristem starts to produce flowers instead of leaves. The timing of floral induction is controlled by sophisticated regulatory networks that monitor changes in the environment, ensuring that flowering occurs under conditions most likely to maximize reproductive success and seed production. In the model plant species Arabidopsis thaliana ?180 genes have been implicated in flowering-time control based on isolation of loss-of-function mutations or analysis of transgenic plants. This SnapShot presents a subset of these genes and proteins, each organized according to its spatial activity in the leaves or the shoot apical meristem of the plant. Strikingly, several genes act more than once and in several tissues during floral induction. Many of these genes occur in a network of six major pathways: the photoperiod and vernalization pathways control flowering in response to seasonal changes in day length and temperature; the ambient temperature pathway responds to daily growth temperatures; and the age, autonomous, and gibberellin pathways act more independently of environmental stimuli. The six pathways converge to regulate a small number of “floral integrator genes,” encoded by different classes of proteins, which govern flowering time by merging signals from multiple pathways. These integrator genes include FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) and SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1 (SOC1), which both rapidly promote floral development. In addition, responses to other environmental stimuli, such as the balance of different wavelengths of light or nutrient availability, also influence flowering time, but how these processes interact with the pathways described here is not fully understood."
- "The switch from vegetative growth (the production of stems and leaves) to reproductive growth (the production of flowers) is an important developmental step in the life cycle of plants. Flowering needs to occur when conditions for pollination and seed development are optimal and consequently most plants restrict flowering to a specific time of year. They commonly achieve this by using reliable environmental cues such as day length (photoperiod) and temperature. In addition, nutrient and water availability and plant size can be important.
- The genes and molecular mechanisms controlling flowering have been extensively studied in the model dicot Arabidopsis thaliana, subsequently Arabidopsis ... As part of this study the Arabidopsis flowering pathways were curated in Arabidopsis Reactome ... to provide an electronic knowledge resource allowing for further developments such as integration with protein-protein interaction datasets, overlaying with microarray data and electronic projection into all newly sequenced plant genomes. Using this we compiled a list of genes and gene families with a known role in flowering time in Arabidopsis.
- Flowering time has also been extensively studied in crop species ... Flowering time is important for adaptation to specific environments and the world's major crop species provide a particularly interesting opportunity for study because they are grown in areas outside the ecogeographical limits of their wild ancestors. In addition, they are adapted to different farming practices such as fall (autumn) sowing or spring sowing in temperate regions. Adaptation to different environments and practices has been achieved by manipulation of flowering time responses and this makes flowering pathways an excellent system for comparison between and within domestic and wild species."
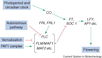
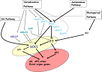
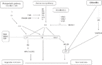
- "Plants switch to the reproductive phase of development when environmental and endogenous factors are the most favourable for reproductive success and seed production. This proper timing is the result of elaborate regulatory networks that coordinate the external stimuli with endogenous cues, inducing the expression of genes that initiate the floral transition at the shoot apical meristem (SAM).
- Much of our current understanding of the floral initiation process is derived from studies using Arabidopsis thaliana as the model system. More than 180 Arabidopsis genes have been identified that play a role in regulating flowering time, and these genes have been organised into six major pathways ... Although the photoperiod and vernalisation pathways monitor seasonal changes in day length or temperature and, hence, initiate flowering in response to exposure to long days or prolonged cold temperatures, the ambient temperature pathway coordinates the response to daily growth temperatures. The autonomous pathway together with those involving age or gibberellin constitutes the rest of the floral pathways, which function more independently of external stimuli. These pathways are integrated by downstream target genes including LEAFY (LFY), FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) and SUPPRESSOR OF CONSTANS1 (SOC1), with their resulting outcomes conveyed to floral meristem identity genes such as APETALA1 (AP1) at the SAM that triggers the flowering process ...
- Flowering is one of the most important agronomic traits influencing crop yield. There is thus a great necessity for research that examines the molecular control of this fundamental process in important crop species. This knowledge is critical for the breeding of climate change resilient crop varieties. Soybean, a major food crop, is also a member of the large and diverse legume family, which has the unique capability of forming nitrogen-fixing symbioses with soil microorganisms and has thus been used as part of sustainable agricultural practices for thousands of years. Soybean is distributed broadly across latitudes and is cultivated as different maturity groups, with each having a narrow range of latitudinal adaptation. Unlike Arabidopsis, soybean can undergo a reversion of flowering when plants are shifted from flowering inductive to non-inductive conditions ... In addition, soybean also follows a floral developmental plan that is distinct from that of Arabidopsis ... Therefore, an understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying these soybean traits is of fundamental and practical interest."
- General plant anatomy / process of flowering
- Why flowering is important to study / general impact
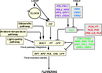
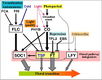
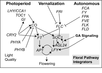
Light Signaling Pathway
- "Light is one of the main environmental regulators of flowering in plants. Plants sense the time of day and season of year by monitoring the light environment through light signalling pathways ... In Arabidopsis, photoperiod pathway genes together with photoreceptor genes and circadian clock components take part in light signalling pathways. The number of known Arabidopsis flowering genes involved in these pathways is 48 ... The key Arabidopsis genes involved in the light signalling pathway include the CONSTANS (CO), PHYTOCHROME (PHY) and CRYPTOCHROME (CRY), CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 (CCA1), LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL (LHY) and PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 1 [PRR1, also called TIMING OF CAB EXPRESSION 1 (TOC1)] genes."
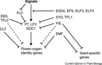
Vernalization Pathway
- "Vernalisation involves plants that require prolonged periods of low temperature to initiate flowering. The vernalisation pathway in Arabidopsis involves 32 genes".
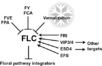
Autonomous Pathway
- "Autonomous pathways in plants are activated in response to endogenous changes that are independent from the environmental cues leading to flowering ... There are 17 genes ... involved in the Arabidopsis autonomous pathway".
Ambient Temperature Pathway
- "Plants respond to ambient temperature changes to modulate their flowering times ... The ambient temperature pathway in Arabidopsis involves 16 genes".
Procedure
- Overall procedure for finding the genes, running with GenSAS, determining SSRs, etc
Gallery of Arabidopsis Flowering Pathways
105 Flowering Genes
This table lists all of the genes involved in the ambient temperature, autonomous, light signaling, and vernalization pathways. All Arabidopsis genes are compiled from Jung et al., 2012. All potential orthologs are found via UniProt Grape nomenclature search.
| Arabidopsis Locus | Other Names | AA Sequence | Pathway | Potential Ortholog |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT1G01060 | LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL, LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 1, LHY, LHY1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G02580 | EMB173, EMBRYO DEFECTIVE 173, FERTILIZATION INDEPENDENT SEED 1, FIS1, MEA, MEDEA, SDG5, SET DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN 5 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT1G04400 | AT-PHH1, ATCRY2, CRY2, CRYPTOCHROME 2, FHA, PHH1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G09570 | ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 8, FAR RED ELONGATED 1, FAR RED ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 2, FHY2, FRE1, HY8, PHYA, PHYTOCHROME A | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT1G13260 | EDF4, ETHYLENE RESPONSE DNA BINDING FACTOR 4, RAV1, RELATED TO ABI3/VP1 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G20330 | COTYLEDON VASCULAR PATTERN 1, CVP1, FRILL1, FRL1, SMT2, STEROL METHYLTRANSFERASE 2 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT1G22770 | FB, GI, GIGANTEA | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G25560 | EDF1, ETHYLENE RESPONSE DNA BINDING FACTOR 1, TEM1, TEMPRANILLO 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G26790 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT1G29160 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT1G30970 | SUF4, SUPPRESSOR OF FRIGIDA4 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT1G31814 | FRIGIDA LIKE 2, FRL2 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT1G47250 | 20S PROTEASOME ALPHA SUBUNIT F2, PAF2 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT1G53090 | SPA1-RELATED 4, SPA4 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G62830 | ARABIDOPSIS LYSINE-SPECIFIC HISTONE DEMETHYLASE, ATLSD1, ATSWP1, LDL1, LSD1, LSD1-LIKE 1, LYSINE-SPECIFIC HISTONE DEMETHYLASE, SWP1 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Autonomous | |
| AT1G65480 | FLOWERING LOCUS T, FT | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator | Grape |
| AT1G68050 | "FLAVIN-BINDING, KELCH REPEAT, F BOX 1", ADO3, FKF1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G68840 | ATRAV2, EDF2, ETHYLENE RESPONSE DNA BINDING FACTOR 2, RAP2.8, RAV2, RELATED TO ABI3/VP1 2, RELATED TO AP2 8, TEM2, TEMPRANILLO 2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT1G77080 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 27, AGL27, FLM, FLOWERING LOCUS M, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 1, MAF1 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | |
| AT1G77300 | ASH1 HOMOLOG 2, ASHH2, CAROTENOID CHLOROPLAST REGULATORY1, CCR1, EARLY FLOWERING IN SHORT DAYS, EFS, LAZ2, LAZARUS 2, SDG8, SET DOMAIN GROUP 8 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT2G06255 | ELF4-L3, ELF4-LIKE 3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G16780 | MSI2, NFC2, NUCLEOSOME/CHROMATIN ASSEMBLY FACTOR GROUP C 2 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT2G17770 | ATBZIP27, BASIC REGION/LEUCINE ZIPPER MOTIF 27, BZIP27, FD PARALOG, FDP | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Meristem identity | |
| AT2G18790 | HY3, OOP1, OUT OF PHASE 1, PHYB, PHYTOCHROME B | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT2G18870 | VEL3, VERNALIZATION5/VIN3-LIKE 3, VIL4, VIN3-LIKE 4 | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT2G18880 | VEL2, VERNALIZATION5/VIN3-LIKE 2, VIL3, VIN3-LIKE 3 | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT2G18915 | ADAGIO 2, ADO2, LKP2, LOV KELCH PROTEIN 2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G19520 | ACG1, ATMSI4, FVE, MSI4, MULTICOPY SUPPRESSOR OF IRA1 4, NFC04, NFC4 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Autonomous | |
| AT2G22540 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 22, AGL22, SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE, SVP | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Vernalization | Grape |
| AT2G23380 | CLF, CURLY LEAF, ICU1, INCURVATA 1, SDG1, SET1, SETDOMAIN 1, SETDOMAIN GROUP 1 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT2G25930 | EARLY FLOWERING 3, ELF3, PYK20 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G32950 | ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1, ATCOP1, CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1, COP1, DEETIOLATED MUTANT 340, DET340, EMB168, EMBRYO DEFECTIVE 168, FUS1, FUSCA 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G33835 | FES1, FRIGIDA-ESSENTIAL 1 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT2G34140 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT2G40080 | EARLY FLOWERING 4, ELF4 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G43410 | FPA | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT2G46340 | SPA1, SUPPRESSOR OF PHYA-105 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G46670 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT2G46790 | APRR9, ARABIDOPSIS PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 9, PRR9, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 9, TL1, TOC1-LIKE PROTEIN 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G46830 | ATCCA1, CCA1, CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT2G47700 | RED AND FAR-RED INSENSITIVE 2, RFI2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G02380 | ATCOL2, B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 3, BBX3, COL2, CONSTANS-LIKE 2 | TAIR | Flowering integrator, Light signaling | |
| AT3G04610 | FLK, FLOWERING LOCUS KH DOMAIN | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT3G07650 | B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 7, BBX7, COL9, CONSTANS-LIKE 9 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G10390 | FLD, FLOWERING LOCUS D | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Autonomous | |
| AT3G12810 | CHR13, PHOTOPERIOD-INDEPENDENT EARLY FLOWERING 1, PIE1, SRCAP | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT3G13682 | LDL2, LSD1-LIKE2 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Autonomous | |
| AT3G15354 | SPA1-RELATED 3, SPA3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G15620 | UV REPAIR DEFECTIVE 3, UVR3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G18990 | REDUCED VERNALIZATION RESPONSE 1, REM39, REPRODUCTIVE MERISTEM 39, VRN1 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT3G20740 | FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM, FERTILIZATION-INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM 1, FIE, FIE1, FIS3 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT3G21320 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT3G24440 | VERNALIZATION 5, VIL1, VIN3-LIKE 1, VRN5 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT3G25730 | EDF3, ETHYLENE RESPONSE DNA BINDING FACTOR 3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G33520 | ACTIN-RELATED PROTEIN 6, ARP6, ATARP6, EARLY IN SHORT DAYS 1, ESD1, SUF3, SUPPRESSOR OF FRI 3 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Vernalization | |
| AT3G46640 | LUX, LUX ARRHYTHMO, PCL1, PHYTOCLOCK 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT3G47500 | CDF3, CYCLING DOF FACTOR 3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT4G00650 | FLA, FLOWERING LOCUS A, FRI, FRIGIDA | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G02020 | EZA1, SDG10, SET DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN 10, SWINGER, SWN | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT4G02560 | LD, LUMINIDEPENDENS | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT4G08920 | ATCRY1, BLU1, BLUE LIGHT UNINHIBITED 1, CRY1, CRYPTOCHROME 1, ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 4, HY4, OOP2, OUT OF PHASE 2 | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT4G11110 | SPA1-RELATED 2, SPA2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT4G11880 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 14, AGL14 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G16250 | PHYD, PHYTOCHROME D | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT4G16280 | FCA | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Autonomous | Grape |
| AT4G16845 | REDUCED VERNALIZATION RESPONSE 2, VRN2 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT4G18130 | PHYE, PHYTOCHROME E | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT4G20370 | TSF, TWIN SISTER OF FT | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator | |
| AT4G22950 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 19, AGL19, GL19 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G24540 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 24, AGL24 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G26000 | PEP, PEPPER | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT4G29730 | MSI5, NFC5, NUCLEOSOME/CHROMATIN ASSEMBLY FACTOR GROUP C5 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Autonomous | |
| AT4G30200 | VEL1, VERNALIZATION5/VIN3-LIKE 1, VIL2, VIN3-LIKE 2 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT4G34530 | CIB1, CRYPTOCHROME-INTERACTING BASIC-HELIX-LOOP-HELIX 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT4G35050 | MSI3, NFC3, NUCLEOSOME/CHROMATIN ASSEMBLY FACTOR GROUP C 3 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT4G35900 | ATBZIP14, FD, FD-1 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Meristem identity | |
| AT5G02810 | APRR7, PRR7, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 7 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G03840 | TERMINAL FLOWER 1, TFL1 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator | Grape |
| AT5G08230 | TAIR | Vernalization | ||
| AT5G08330 | CCA1 HIKING EXPEDITION, CHE, TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR TCP21, TCP21 | UniProtKB | Light signaling | |
| AT5G10140 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 25, AGL25, FLC, FLF, FLOWERING LOCUS C, FLOWERING LOCUS F | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | Grape |
| AT5G13480 | FY | TAIR | Autonomous | |
| AT5G15840 | B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 1, BBX1, CO, CONSTANS, FG | TAIR | Flowering integrator, Light signaling | |
| AT5G15850 | ATCOL1, B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 2, BBX2, COL1, CONSTANS-LIKE 1 | TAIR | Flowering integrator, Light signaling | |
| AT5G23150 | ENHANCER OF AG-4 2, HUA2 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT5G23280 | TAIR | Light signaling | ||
| AT5G24470 | APRR5, PRR5, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 5 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G24930 | ATCOL4, B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 5, BBX5, COL4, CONSTANS-LIKE 4 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G35840 | PHYC, PHYTOCHROME C | TAIR | Light signaling | Grape |
| AT5G37055 | ATSWC6, SEF, SERRATED LEAVES AND EARLY FLOWERING | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT5G39660 | CDF2, CYCLING DOF FACTOR 2 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G42790 | ARS5, ARSENIC TOLERANCE 5, ATPSM30, PAF1, PROTEASOME ALPHA SUBUNIT F1 | TAIR | Vernalization | |
| AT5G48250 | B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 8, BBX8 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G57360 | ADAGIO 1, ADO1, FKF1-LIKE PROTEIN 2, FKL2, LKP1, LOV KELCH PROTEIN 1, ZEITLUPE, ZTL | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G57380 | VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3, VIN3 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT5G57660 | ATCOL5, B-BOX DOMAIN PROTEIN 6, BBX6, COL5, CONSTANS-LIKE 5 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G58230 | ARABIDOPSIS MULTICOPY SUPRESSOR OF IRA1, ATMSI1, MATERNAL EFFECT EMBRYO ARREST 70, MEE70, MSI1, MULTICOPY SUPRESSOR OF IRA1 | TAIR | Autonomous, Vernalization | |
| AT5G59570 | BOA, BROTHER OF LUX ARRHYTHMO | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G60100 | APRR3, PRR3, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 3 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G61380 | APRR1, ATTOC1, PRR1, PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATOR 1, TIMING OF CAB EXPRESSION 1, TOC1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G62430 | CDF1, CYCLING DOF FACTOR 1 | TAIR | Light signaling | |
| AT5G65050 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 31, AGL31, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 2, MAF2 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | |
| AT5G65060 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 70, AGL70, FCL3, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 3, MAF3 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | |
| AT5G65070 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 69, AGL69, FCL4, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 4, MAF4 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization | |
| AT5G65080 | AGAMOUS-LIKE 68, AGL68, MADS AFFECTING FLOWERING 5, MAF5 | TAIR | Ambient temperature, Flowering integrator, Vernalization |