Time of bloom
By Austin Mudd - Spring 2013
Contents
To Do
- Write introduction and procedure sections
- Aggregate all sequences into a single document in proper FASTA format
Introduction
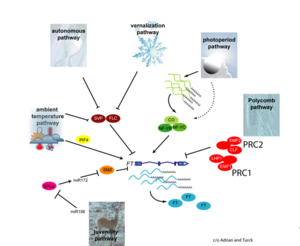
- Higgins et al., 2010
- Jung et al., 2012
- General plant anatomy / process of flowering
- Why flowering is important to study / general impact
- Factors affecting time of flowering
Procedure
- Overall procedure for finding the genes, running with GenSAS, determining SSRs, etc
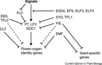
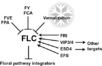
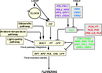
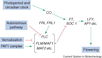
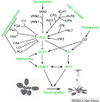
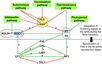
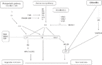
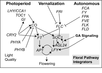
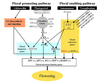
Gallery of Arabidopsis Flowering Pathways
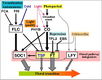
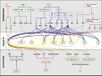
105 Flowering Genes
The below table lists all of the genes involved in the ambient temperature, autonomous, light signaling, and vernalization pathways.
Note: All Arabidopsis genes are compiled from Jung et al., 2012. All potential orthologs are found via UniProt Grape or UniProt Strawberry nomenclature search. Formatting is the same as Jung et al., 2012 where a * indicates 1 of "24 Arabidopsis genes, which had not been previously investigated for their roles in flowering, [that] belong to [paralog groups] with known Arabidopsis flowering genes." Moreover, for pathways, "Am: Ambient temperature pathway, Au: Autonomous pathway, FPI: Flowering Pathway [Integrators], L: Light signaling pathway, MI: Meristem Identity, V: Vernalization pathway."
| Pathway | Arabidopsis Gene | Function (All function information is directly copied from the respective AA Sequence website link) | AA Sequence | Potential Ortholog |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Am, Au | FCA | "Involved in the promotion of the transition of the vegetative meristem to reproductive development. Four forms of the protein (alpha, beta, delta and gamma) are produced by alternative splicing. Involved in RNA-mediated chromatin silencing. At one point it was believed to act as an abscisic acid receptor but the paper describing that function was retracted." | TAIR | Grape |
| Am, Au | FLD | "Encodes a plant homolog of a SWIRM domain containing protein found in histone deacetylase complexes in mammals. Lesions in FLD result in hyperacetylation of histones in FLC chromatin, up-regulation of FLC expression and extremely delayed flowering. FLD plays a key role in regulating the reproductive competence of the shoot and results in different developmental phase transitions in Arabidopsis." | TAIR | |
| Am, Au | FVE | "Controls flowering." | TAIR | |
| Am, Au | LDL1* | "Encodes a homolog of human Lysine-Specific Demethylase1. Involved in H3K4 methylation of target genes including the flowering time loci FLC and FWA. Located in nucleus. Negatively regulates root elongation. Involved in repression of LRP1 via histone deacetylation." | TAIR | |
| Am, Au | LDL2* | "Encodes a homolog of human Lysine-Specific Demethylase1. Involved in H3K4 methylation of target genes including the flowering loci FLC and FWA." | TAIR | |
| Am, Au | NFC5* | "Cell cycle-related repressor genes encoding WD-repeat proteins." | TAIR | |
| Am, FPI | FT | "FT, together with LFY, promotes flowering and is antagonistic with its homologous gene, TERMINAL FLOWER1 (TFL1). FT is expressed in leaves and is induced by long day treatment. Either the FT mRNA or protein is translocated to the shoot apex where it induces its own expression. Recent data suggests that FT protein acts as a long-range signal. FT is a target of CO and acts upstream of SOC1." | TAIR | Grape, Strawberry |
| Am, FPI | TFL1 | "Controls inflorescence meristem identity. Involved in the floral initiation process. Ortholog of the Antirrhinum gene CENTRORADIALIS (CEN). Involved in protein trafficking to the protein storage vacuole." | TAIR | Grape, Strawberry |
| Am, FPI | TSF | "Encodes a floral inducer that is a homolog of FT. Plants overexpressing this gene flower earlier than Col. Loss-of-function mutations flower later in short days. TSF and FT play overlapping roles in the promotion of flowering, with FT playing the dominant role. TSF sequences show extensive variation in different accessions and may contribute to quantitative variation in flowering time in these accessions. TSF has a complex pattern of spatial expression; it is expressed mainly in phloem and expression is regulated by daylength and vernalization." | TAIR | |
| Am, FPI, V | AGL31 | "Probable transcription factor that prevents vernalization by short periods of cold. Acts as a floral repressor." | UniProtKB | |
| Am, FPI, V | FLC | "MADS-box protein encoded by FLOWERING LOCUS C - transcription factor that functions as a repressor of floral transition and contributes to temperature compensation of the circadian clock. Expression is downregulated during cold treatment. Vernalization, FRI and the autonomous pathway all influence the state of FLC chromatin. Both maternal and paternal alleles are reset by vernalization, but their earliest activation differs in timing and location. Histone H3 trimethylation at lysine 4 and histone acetylation are associated with active FLC expression, whereas histone deacetylation and histone H3 dimethylation at lysines 9 and 27 are involved in FLC repression. Expression is also repressed by two small RNAs (30- and 24-nt) complementary to the FLC sense strand 3’ to the polyA site. The small RNAs are most likely derived from an antisense transcript of FLC. Interacts with SOC1 and FT chromatin in vivo. Member of a protein complex." | TAIR | Grape |
| Am, FPI, V | MAF1 | "MADS domain protein - flowering regulator that is closely related to FLC. Deletion of this locus in Nd ecotype is correlated with earlier flowering in short days suggesting function as a negative regulator of flowering." | TAIR | |
| Am, FPI, V | MAF3 | "MADS domain protein - flowering regulator that is closely related to FLC" | TAIR | |
| Am, FPI, V | MAF4 | "Encodes MADS-box containing FLC paralog. Five splice variants have been identified but not characterized with respect to expression patterns and/or differing function. Overexpression of the gene in the Landsberg ecotype leads to a delay in flowering, transcript levels of MAF4 are reduced after a 6 week vernalization." | TAIR | |
| Am, FPI, V | MAF5 | "Is upregulated during vernalization and regulates flowering time. Encodes MADS-domain protein. Two variants encoding proteins of 198 and 184 amino acids have been reported." | TAIR | |
| Am, MI | ATBZIP27 | "Transcription factor" | GenScript | |
| Am, MI | FD | "bZIP protein required for positive regulation of flowering. Mutants are late flowering. FD interacts with FT to promote flowering. Expressed in the shoot apex in floral anlagen, then declines in floral primordia." | TAIR | |
| Am, V | ATARP6 | "Component of the SWR1 complex which mediates the ATP-dependent exchange of histone H2A for the H2A variant H2A.F/Z leading to transcriptional regulation of selected genes (e.g. FLC) by chromatin remodeling. Required for the activation of FLC and FLC/MAF genes expression to levels that inhibit flowering, through both histone H3 and H4 acetylation and methylation mechanisms. Involved in several developmental processes including organization of plant organs, leaves formation, flowering time repression, and fertility. Modulates photoperiod-dependent epidermal leaves cell development; promotes cell division in long days, and cell expansion/division in short days. May be involved in the regulation of pathogenesis-related proteins (PRs)." | UniProtKB | |
| Am, V | SVP | "Encodes a nuclear protein that acts as a floral repressor and that functions within the thermosensory pathway. SVP represses FT expression via direct binding to the vCArG III motif in the FT promoter." | TAIR | Grape |
| Au | FLK | "RNA binding, nucleic acid binding; positive regulation of flower development" | TAIR | |
| Au | FPA | "FPA is a gene that regulates flowering time in Arabidopsis via a pathway that is independent of daylength (the autonomous pathway). Mutations in FPA result in extremely delayed flowering. Double mutants with FCA have reduced fertility and single/double mutants have defects in siRNA mediated chromatin silencing." | TAIR | |
| Au | FY | "Encodes a protein with similarity to yeast Pfs2p, an mRNA processing factor. Involved in regulation of flowering time; affects FCA mRNA processing. Homozygous mutants are late flowering, null alleles are embryo lethal." | TAIR | |
| Au | LD | "Encodes a nuclear localized protein with similarity to transcriptional regulators. Recessive mutants are late flowering. Expression of LFY is reduced in LD mutants." | TAIR | |
| Au | VEL2 | "Protein of unknown function" | TAIR | |
| Au | VEL3 | "Protein of unknown function" | TAIR | |
| Au, V | CLF | "Similar to the product of the Polycomb-group gene Enhancer of zeste. Required for stable repression of AG and AP3. Putative role in cell fate determination. Involved in the control of leaf morphogenesis. mutants exhibit curled, involute leaves. AGAMOUS and APETALA3 are ectopically expressed in the mutant." | TAIR | |
| Au, V | FIE1 | "Encodes a protein similar to the transcriptional regular of the animal Polycomb group and is involved in regulation of establishment of anterior-posterior polar axis in the endosperm and repression of flowering during vegetative phase. Mutation leads endosperm to develop in the absence of fertilization and flowers to form in seedlings and non-reproductive organs. Also exhibits maternal effect gametophytic lethal phenotype, which is suppressed by hypomethylation. Forms part of a large protein complex that can include VRN2 (VERNALIZATION 2), VIN3 (VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3) and polycomb group proteins FERTILIZATION INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM (FIE), CURLY LEAF (CLF) and SWINGER (SWN or EZA1). The complex has a role in establishing FLC (FLOWERING LOCUS C) repression during vernalization. In the ovule, the FIE transcript levels increase transiently just after fertilization." | TAIR | |
| Au, V | MEA* | "Encodes a putative transcription factor MEDEA (MEA) that negatively regulates seed development in the absence of fertilization. Mutations in this locus result in embryo lethality. MEA is a Polycomb group gene that is imprinted in the endosperm. The maternal allele is expressed and the paternal allele is silent. MEA is controlled by DEMETER (DME), a DNA glycosylase required to activate MEA expression, and METHYLTRANSFERASE I (MET1), which maintains CG methylation at the MEA locus. MEA is involved in the negative regulation of its own imprinted gene expression; the effect is not only allele-specific but also dynamically regulated during seed development. In the ovule, the MEA transcripts are accumulated at their highest level before fertilization and gradually decrease after fertilization" | TAIR | |
| Au, V | MSI1 | "Encodes a WD-40 repeat containing protein that functions in chromatin assembly as part of the CAF1 and FIE complex. Mutants exhibit parthenogenetic development that includes proliferation of unfertilized endosperm and embryos. In heterozygous plants 50% of embryos abort. Of the aborted embryos the early aborted class are homozygous and the later aborting lass are heterozygotes in which the defective allele is maternally transmitted. Other phenotypes include defects in ovule morphogenesis and organ initiation, as well as increased levels of heterochromatic DNA. MSI1 is needed for the transition to flowering. In Arabidopsis, the three CAF-1 subunits are encoded by FAS1, FAS2 and, most likely, MSI1, respectively. Mutations in FAS1 or FAS2 lead to increased frequency of homologous recombination and T-DNA integration in Arabidopsis. In the ovule, the MSI1 transcripts are accumulated at their highest level before fertilization and gradually decrease after fertilization. MSI is biallelically expressed, the paternal allele is expressed in the endosperm and embryo and is not imprinted. MSI1 forms a complex with RBR1 that is required for activation of the imprinted genes FIS2 and FWA. This activation is mediated by MSI1/RBR1 mediated repression of MET1." | TAIR | |
| Au, V | MSI2* | "Core histone-binding subunit that may target chromatin assembly factors, chromatin remodeling factors and histone deacetylases to their histone substrates in a manner that is regulated by nucleosomal DNA" | UniProtKB | |
| Au, V | MSI3* | "Core histone-binding subunit that may target chromatin assembly factors, chromatin remodeling factors and histone deacetylases to their histone substrates in a manner that is regulated by nucleosomal DNA" | UniProtKB | |
| Au, V | SWN | "Encodes a polycomb group protein. Forms part of a large protein complex that can include VRN2 (VERNALIZATION 2), VIN3 (VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3) and polycomb group proteins FERTILIZATION INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM (FIE) and CURLY LEAF (CLF). The complex has a role in establishing FLC (FLOWERING LOCUS C) repression during vernalization. Performs a partially redundant role to MEA in controlling seed initiation by helping to suppress central cell nucleus endosperm proliferation within the FG." | TAIR | |
| Au, V | VEL1 | "Encodes a protein with similarity to VRN5 and VIN3.Contains both a fibronectin III and PHD finger domain. VEL1 is a part of a polycomb repressive complex (PRC2) that is involved in epigenetic silencing of the FLC flowering locus." | TAIR | |
| Au, V | VIN3 | "Encodes a plant homeodomain protein VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3 (VIN3). In planta VIN3 and VRN2, VERNALIZATION 2, are part of a large protein complex that can include the polycomb group (PcG) proteins FERTILIZATION INDEPENDENT ENDOSPERM (FIE), CURLY LEAF (CLF), and SWINGER (SWN or EZA1). The complex has a role in establishing FLC (FLOWERING LOCUS C) repression during vernalization." | TAIR | |
| Au, V | VRN2 | "The VERNALIZATION2 (VRN2) gene mediates vernalization and encodes a nuclear-localized zinc finger protein with similarity to Polycomb group (PcG) proteins of plants and animals. In wild-type Arabidopsis, vernalization results in the stable reduction of the levels of the floral repressor FLC. In vrn2 mutants, FLC expression is downregulated normally in response to vernalization, but instead of remaining low, FLC mRNA levels increase when plants are returned to normal temperatures. VRN2 maintains FLC repression after a cold treatment, serving as a mechanism for the cellular memory of vernalization. Required for complete repression of FLC. Required for the methylation of histone H3." | TAIR | |
| Au, V | VRN5 | "Encodes Vernalization Insensitive 3-like 1 (VIL1). VIL1 is involved in the photoperiod and vernalization of Arabidopsis by regulating expression of the related floral repressors Flowering Locus C (FLC) and Flowering Locus M (FLM). VIL1, along with VIN3 (Vernalization Insensitive 3) is necessary for the chromatin modification to FLC and FLM." | TAIR | |
| FPI, L | CO | "Encodes a protein showing similarities to zinc finger transcription factors, involved in regulation of flowering under long days. Acts upstream of FT and SOC1." | TAIR | |
| FPI, L | COL1 | "Homologous to the flowering-time gene CONSTANS." | TAIR | |
| FPI, L | COL2 | "Homologous to the flowering-time gene CONSTANS (CO) encoding zinc-finger proteins" | TAIR | |
| L | APRR3 | "Controls photoperiodic flowering response. Component of the circadian clock. Controls the degradation of APRR1/TOC1 by the SCF(ZTL) complex. Expression of several members of the ARR-like family is controlled by circadian rhythm. The particular coordinated sequential expression of APRR9, APRR7, APRR5, APRR3 and APPR1 result to circadian waves that may be at the basis of the endogenous circadian clock." | UniProtKB | |
| L | APRR5 | "Controls photoperiodic flowering response. Seems to be one of the component of the circadian clock. Expression of several members of the ARR-like family is controlled by circadian rhythm. The particular coordinated sequential expression of APRR9, APRR7, APRR5, APRR3 and APPR1 result to circadian waves that may be at the basis of the endogenous circadian clock." | UniProtKB | |
| L | APRR9 | "Controls photoperiodic flowering response. Seems to be one of the component of the circadian clock. Expression of several members of the ARR-like family is controlled by circadian rhythm. The particular coordinated sequential expression of APRR9, APRR7, APRR5, APRR3 and APPR1 result to circadian waves that may be at the basis of the endogenous circadian clock." | UniProtKB | |
| L | AT1G26790 | "Transcription factor that binds specifically to a 5'-AA[AG]G-3' consensus core sequence." | UniProtKB | |
| L | AT1G29160 | "Transcription factor that binds specifically to a 5'-AA[AG]G-3' consensus core sequence. Acts as a negative regulator in the phytochrome-mediated light responses. Controls phyB-mediated end-of-day response and the phyA-mediated anthocyanin accumulation." | UniProtKB | |
| L | AT2G34140 | "Transcription factor that binds specifically to a 5'-AA[AG]G-3' consensus core sequence." | UniProtKB | |
| L | AT2G46670* | "Putative uncharacterized protein" | UniProtKB | |
| L | AT3G21320 | "Uncharacterized protein" | UniProtKB | |
| L | AT3G25730 | "Probably acts as a transcriptional activator. Binds to the GCC-box pathogenesis-related promoter element. May be involved in the regulation of gene expression by stress factors and by components of stress signal transduction pathways." | UniProtKB | |
| L | AT5G23280* | "Transcription factor" | UniProtKB | |
| L | AT5G48250* | "Zinc finger protein Constans-like 10" | UniProtKB | |
| L | AT5G59570* | "Putative transcription factor" | UniProtKB | |
| L | ATCOL4 | "Sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity, zinc ion binding." | TAIR | |
| L | ATCOL5 | "Sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity, zinc ion binding." | TAIR | |
| L | CCA1 | "Transcription factor involved in the circadian clock and in the phytochrome regulation. Binds to the promoter regions of APRR1/TOC1 and TCP21/CHE to repress their transcription. Binds to the promoter regions of CAB2A and CAB2B to promote their transcription. Represses both LHY and itself." | UniProtKB | |
| L | CDF1 | "Cell growth defect factor" | UniProtKB | |
| L | CDF2 | "Cell growth defect factor" | UniProtKB | |
| L | CDF3 | "Plant non-specific lipid-transfer proteins transfer phospholipids as well as galactolipids across membranes. May play a role in wax or cutin deposition in the cell walls of expanding epidermal cells and certain secretory tissues." | UniProtKB | |
| L | CHE | "Transcription factor involved in the regulation of the circadian clock. Acts as a repressor of CCA1 by binding to its promoter. No binding to the LHY promoter." | UniProtKB | |
| L | CIB1 | "Encodes a transcription factor CIB1 (cryptochrome-interacting basic-helix-loop-helix). CIB1 interacts with CRY2 (cryptochrome 2) in a blue light-specific manner in yeast and Arabidopsis cells, and it acts together with additional CIB1-related proteins to promote CRY2-dependent floral initiation. CIB1 positively regulates FT expression." | TAIR | |
| L | COL9 | "This gene belongs to the CO (CONSTANS) gene family. This gene family is divided in three subgroups: groups III, to which COL9 belongs, is characterized by one B-box (supposed to regulate protein-protein interactions) and a second diverged zinc finger. COL9 downregulates expression of CO (CONSTANS) as well as FT and SOC1 which are known regulatory targets of CO." | TAIR | |
| L | COP1 | "Represses photomorphogenesis and induces skotomorphogenesis in the dark. Contains a ring finger zinc-binding motif, a coiled-coil domain, and several WD-40 repeats, similar to G-beta proteins. The C-terminus has homology to TAFII80, a subunit of the TFIID component of the RNA polymerase II of Drosophila. Nuclear localization in the dark and cytoplasmic in the light." | TAIR | |
| L | CRY1 | "Encodes CRY1, a flavin-type blue-light photoreceptor with ATP binding and autophosphorylation activity. Functions in perception of blue / green ratio of light. The photoreceptor may be involved in electron transport. Mutant phenotype displays a blue light-dependent inhibition of hypocotyl elongation. Photoreceptor activity requires light-induced homodimerisation of the N-terminal CNT1 domains of CRY1. Involved in blue-light induced stomatal opening. The C-terminal domain of the protein undergoes a light dependent conformational change. Also involved in response to circadian rhythm. Mutants exhibit long hypocotyl under blue light and are out of phase in their response to circadian rhythm. CRY1 is present in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Different subcellular pools of CRY1 have different functions during photomorphogenesis of Arabidopsis seedlings." | TAIR | Grape |
| L | CRY2 | "Blue light receptor mediating blue-light regulated cotyledon expansion and flowering time. Positive regulator of the flowering-time gene CONSTANS. This gene possesses a light-induced CNT2 N-terminal homodimerisation domain. Involved in blue-light induced stomatal opening. Involved in triggering chromatin decondensation. An 80-residue motif (NC80) is sufficient to confer CRY2's physiological function. It is proposed that the PHR domain and the C-terminal tail of the unphosphorylated CRY2 form a "closed" conformation to suppress the NC80 motif in the absence of light. In response to blue light, the C-terminal tail of CRY2 is phosphorylated and electrostatically repelled from the surface of the PHR domain to form an "open" conformation, resulting in derepression of the NC80 motif and signal transduction to trigger photomorphogenic responses. Cry2 phosphorylation and degradation both occur in the nucleus." | TAIR | |
| L | ELF3 | "Encodes a nuclear protein that is expressed rhythmically and interacts with phytochrome B to control plant development and flowering through a signal transduction pathway. Required component of the core circadian clock regardless of light conditions." | TAIR | |
| L | ELF4 | "Encodes a novel nuclear 111 amino-acid phytochrome-regulated component of a negative feedback loop involving the circadian clock central oscillator components CCA1 and LHY. ELF4 is necessary for light-induced expression of both CCA1 and LHY, and conversely, CCA1 and LHY act negatively on light-induced ELF4 expression. ELF4 promotes clock accuracy and is required for sustained rhythms in the absence of daily light/dark cycles. It is involved in the phyB-mediated constant red light induced seedling de-etiolation process and may function to coregulate the expression of a subset of phyB-regulated genes." | TAIR | |
| L | ELF4-L3 | "Protein of unknown function" | TAIR | |
| L | FKF1 | "Encodes FKF1, a flavin-binding kelch repeat F box protein, is clock-controlled, regulates transition to flowering. Forms a complex with GI on the CO promoter to regulate CO expression." | TAIR | |
| L | GI | "Together with CONSTANTS (CO) and FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), GIGANTEA promotes flowering under long days in a circadian clock-controlled flowering pathway. GI acts earlier than CO and FT in the pathway by increasing CO and FT mRNA abundance. Located in the nucleus. Regulates several developmental processes, including photoperiod-mediated flowering, phytochrome B signaling, circadian clock, carbohydrate metabolism, and cold stress response. The gene's transcription is controlled by the circadian clock and it is post-transcriptionally regulated by light and dark. Forms a complex with FKF1 on the CO promoter to regulate CO expression." | TAIR | |
| L | LHY | "LHY encodes a myb-related putative transcription factor involved in circadian rhythm along with another myb transcription factor CCA1." | TAIR | |
| L | LKP2 | "Encodes a member of F-box proteins that includes two other proteins in Arabidopsis (ZTL and FKF1). These proteins contain a unique structure containing a PAS domain at their N-terminus, an F-box motif, and 6 kelch repeats at their C-terminus. Overexpression results in arrhythmic phenotypes for a number of circadian clock outputs in both constant light and constant darkness, long hypocotyls under multiple fluences of both red and blue light, and a loss of photoperiodic control of flowering time. Although this the expression of this gene itself is not regulated by circadian clock, it physically interacts with Dof transcription factors that are transcriptionally regulated by circadian rhythm. LKP2 interacts with Di19, CO/COL family proteins." | TAIR | |
| L | LUX | "Encodes a myb family transcription factor with a single Myb DNA-binding domain (type SHAQKYF) that is unique to plants and is essential for circadian rhythms, specifically for transcriptional regulation within the circadian clock. LUX is required for normal rhythmic expression of multiple clock outputs in both constant light and darkness. It is coregulated with TOC1 and seems to be repressed by CCA1 and LHY by direct binding of these proteins to the evening element in the LUX promoter." | TAIR | |
| L | PHYA | "Light-labile cytoplasmic red/far-red light photoreceptor involved in the regulation of photomorphogenesis. It exists in two inter-convertible forms: Pr and Pfr (active) and functions as a dimer. The N terminus carries a single tetrapyrrole chromophore, and the C terminus is involved in dimerization. It is the sole photoreceptor mediating the FR high irradiance response (HIR). Major regulator in red-light induction of phototropic enhancement. Involved in the regulation of de-etiolation. Involved in gravitropism and phototropism. Requires FHY1 for nuclear accumulation." | TAIR | Grape |
| L | PHYB | "Red/far-red photoreceptor involved in the regulation of de-etiolation. Exists in two inter-convertible forms: Pr and Pfr (active). Involved in the light-promotion of seed germination and in the shade avoidance response. Promotes seedling etiolation in both the presence and absence of phytochrome A. Overexpression results in etiolation under far-red light. Accumulates in the nucleus after exposure to far red light." | TAIR | Grape |
| L | PHYC | "Encodes the apoprotein of phytochrome; one of a family of photoreceptors that modulate plant growth and development." | TAIR | Grape |
| L | PHYD | "Encodes a phytochrome photoreceptor with a function similar to that of phyB that absorbs the red/far-red part of the light spectrum and is involved in light responses. It cannot compensate for phyB loss in Arabidopsis but can substitute for tobacco phyB in vivo." | TAIR | |
| L | PHYE | "Histidine kinase" | TAIR | Grape |
| L | PRR7 | "PRR7 and PRR9 are partially redundant essential components of a temperature-sensitive circadian system. CCA1 and LHY had a positive effect on PRR7 expression levels. Acts as transcriptional repressor of CCA1 and LHY." | TAIR | |
| L | RAV1 | "Encodes an AP2/B3 domain transcription factor which is upregulated in response to low temperature. It contains a B3 DNA binding domain. It has circadian regulation and may function as a negative growth regulator." | TAIR | |
| L | RFI2 | "Zinc ion binding" | TAIR | |
| L | SPA1 | "Encodes a member of the SPA (suppressor of phyA-105) protein family (SPA1-SPA4). SPA proteins contain an N-terminal serine/threonine kinase-like motif followed by a coiled-coil structure and a C-terminal WD-repeat domain. SPA1 is a PHYA signaling intermediate, putative regulator of PHYA signaling pathway. Light responsive repressor of photomorphogenesis. Involved in regulating circadian rhythms and flowering time in plants. Under constant light, the abundance of SPA1 protein exhibited circadian regulation, whereas under constant darkness, SPA1 protein levels remained unchanged. In addition, the spa1-3 mutation slightly shortened circadian period of CCA1, TOC1/PRR1 and SPA1 transcript accumulation under constant light." | TAIR | |
| L | SPA2 | "Encodes a member of the SPA (suppressor of phyA-105) protein family (SPA1-SPA4). SPA proteins contain an N-terminal serine/threonine kinase-like motif followed by a coiled-coil structure and a C-terminal WD-repeat domain. SPA proteins function redundantly in suppressing photomorphogenesis in dark- and light-grown seedlings. SPA2 primarily regulates seedling development in darkness and has little function in light-grown seedlings or adult plants." | TAIR | |
| L | SPA3 | "Encodes a member of the SPA (suppressor of phyA-105) protein family (SPA1-SPA4). SPA proteins contain an N-terminal serine/threonine kinase-like motif followed by a coiled-coil structure and a C-terminal WD-repeat domain. SPA proteins function redundantly in suppressing photomorphogenesis in dark- and light-grown seedlings. SPA3 (and SPA4) predominantly regulates elongation growth in adult plants." | TAIR | |
| L | SPA4 | "Encodes a member of the SPA (suppressor of phyA-105) protein family (SPA1-SPA4). SPA proteins contain an N-terminal serine/threonine kinase-like motif followed by a coiled-coil structure and a C-terminal WD-repeat domain. SPA proteins function redundantly in suppressing photomorphogenesis in dark- and light-grown seedlings. SPA4 (and SPA3) predominantly regulates elongation growth in adult plants." | TAIR | |
| L | TEM1 | "Encodes a member of the RAV transcription factor family that contains AP2 and B3 binding domains. Involved in the regulation of flowering under long days. Loss of function results in early flowering. Overexpression causes late flowering and repression of expression of FT. Novel transcriptional regulator involved in ethylene signaling. Promoter bound by EIN3. EDF1 in turn, binds to promoter elements in ethylene responsive genes." | TAIR | |
| L | TEM2 | "Rav2 is part of a complex that has been named `regulator of the (H+)-ATPase of the vacuolar and endosomal membranes' (RAVE)" | TAIR | |
| L | TOC1 | "Pseudo response regulator involved in the generation of circadian rhythms. TOC1 appears to shorten the period of circumnutation speed. TOC1 contributes to the plant fitness (carbon fixation, biomass) by influencing the circadian clock period. PRR3 may increase the stability of TOC1 by preventing interactions between TOC1 and the F-box protein ZTL. Expression of TOC1 is correlated with rhythmic changes in chromatin organization." | TAIR | |
| L | UVR3* | "Required for photorepair of 6-4 photoproducts in Arabidopsis thaliana." | TAIR | |
| L | ZTL | "Encodes clock-associated PAS protein ZTL; Also known as FKF1-like protein 2 or ADAGIO1(ADO1). A protein containing a PAS domain ZTL contributes to the plant fitness (carbon fixation, biomass) by influencing the circadian clock period. ZTL is the F-box component of an SCF complex implicated in the degradation of TOC1." | TAIR | |
| V | AGL14 | "Probable transcription factor." | UniProtKB | |
| V | AGL19 | "Probable transcription factor that promotes flowering, especially in response to vernalization by short periods of cold, in an FLC-independent manner." | UniProtKB | |
| V | AGL24 | "Transcription activator that mediates floral transition in response to vernalization. Promotes inflorescence fate in apical meristems. Acts in a dosage-dependent manner. Probably involved in the transduction of RLK-mediated signaling (e.g. IMK3 pathway). Together with AP1 and SVP, controls the identity of the floral meristem and regulates expression of class B, C and E genes. When associated with SOC1, mediates effect of gibberellins on flowering under short-day conditions, and regulates the expression of LEAFY (LFY), which links floral induction and floral development. Confers inflorescence characteristics to floral primordia and early flowering." | UniProtKB | |
| V | AT5G08230* | "Probable transcription factor that seems to be involved in mRNA processing." | UniProtKB | |
| V | ATSWC6 | "Encodes SERRATED LEAVES AND EARLY FLOWERING (SEF), an Arabidopsis homolog of the yeast SWC6 protein, a conserved subunit of the SWR1/SRCAP complex. SEF loss-of-function mutants have a pleiotropic phenotype characterized by serrated leaves, frequent absence of inflorescence internodes, bushy aspect, and flowers with altered number and size of organs. sef plants flower earlier than wild-type plants both under inductive and non-inductive photoperiods. SEF, ARP6 and PIE1 might form a molecular complex in Arabidopsis related to the SWR1/SRCAP complex identified in other eukaryotes." | TAIR | |
| V | EFS | "Encodes a protein with histone lysine N-methyltransferase activity required specifically for the trimethylation of H3-K4 in FLC chromatin (and not in H3-K36 dimethylation). Acts as an inhibitor of flowering specifically involved in the autonomous promotion pathway. EFS also regulates the expression of genes involved in carotenoid biosynthesis. Modification of histone methylation at the CRTISO locus reduces transcript levels 90%. The increased shoot branching seen in some EFS mutants is likely due to the carotenoid biosynthesis defect having an effect on stringolactones. Required for ovule, embryo sac, anther and pollen development." | TAIR | |
| V | FES1 | "Encodes a zinc finger domain containing protein that is expressed in the shoot/root apex and vasculature, and acts with FRI to repress flowering.FES1 mutants in a Col(FRI+) background will flower early under inductive conditions." | TAIR | |
| V | FRI | "Encodes a major determinant of natural variation in Arabidopsis flowering time. Dominant alleles of FRI confer a vernalization requirement causing plants to overwinter vegetatively. Many early flowering accessions carry loss-of-function fri alleles .Twenty distinct haplotypes that contain non-functional FRI alleles have been identified and the distribution analyzed in over 190 accessions. The common lab strains- Col and Ler each carry loss of function mutations in FRI." | TAIR | |
| V | FRL1 | "Encodes a sterol-C24-methyltransferases involved in sterol biosynthesis. Mutants display altered sterol composition, serrated petals and sepals and altered cotyledon vascular patterning as well as ectopic endoreduplication. This suggests that suppression of endoreduplication is important for petal morphogenesis and that normal sterol composition is required for this suppression." | TAIR | |
| V | FRL2 | "Family member of FRI-related genes that is required for the winter-annual habit. " | TAIR | |
| V | HUA2 | "Putative transcription factor. Member of the floral homeotic AGAMOUS pathway. Mutations in HUA enhance the phenotype of mild ag-4 allele. Single hua mutants are early flowering and have reduced levels of FLC mRNA. Other MADS box flowering time genes such as FLM and MAF2 also appear to be regulated by HUA2. HUA2 normally activates FLC expression and enhances AG function." | TAIR | |
| V | PAF1 | "Encodes a protein with extensive homology to the largest subunit of the multicatalytic proteinase complex (proteasome). Negatively regulates thiol biosynthesis and arsenic tolerance." | TAIR | |
| V | PAF2 | "Encodes 20S proteasome subunit PAF2 (PAF2)." | TAIR | |
| V | PEP | "Encodes a novel Arabidopsis gene encoding a polypeptide with K-homology (KH) RNA-binding modules, which acts on vegetative growth and pistil development. Genetic studies suggest that PEP interacts with element(s) of the CLAVATA signaling pathway." | TAIR | |
| V | PIE1 | "Encodes a protein similar to ATP-dependent, chromatin-remodeling proteins of the ISWI and SWI2/SNF2 family. Genetic analyses suggest that this gene is involved in multiple flowering pathways. Mutations in PIE1 results in suppression of FLC-mediated delay of flowering and causes early flowering in noninductive photoperiods independently of FLC. PIE1 is required for expression of FLC in the shoot apex but not in the root. Along with ARP6 forms a complex to deposit modified histone H2A.Z at several loci within the genome. This modification alters the expression of the target genes (i.e. FLC, MAF4, MAF6)." | TAIR | |
| V | SUF4 | "Encodes SUF4 (SUPPRESSOR of FRI 4), a putative zinc-finger-containing transcription factor that is required for delayed flowering in winter-annual Arabidopsis. suf4 mutations strongly suppress the late-flowering phenotype of FRI (FRIGIDA) mutants. suf4 mutants also show reduced H3K4 trimethylation at FLC (FLOWERING LOCUS C), a floral inhibitor. SUF4 may act to specifically recruit a putative histone H3 methyltransferase EFS (EARLY FLOWERING IN SHORT DAYS) and the PAF1-like complex to the FLC locus." | TAIR | |
| V | VRN1 | "Required for vernalization. Essential for the complete repression of FLC in vernalized plants. Required for the methylation of histone H3." | TAIR |