Davidson Missouri W/Solving the HPP in vivo
Using the same flipping mechanism, we are trying to develop a bacterial computer which solves a new type of mathematical problem, the Hamiltonian Path problem
Contents
The Hamiltonian Path Problem
A Hamiltonian Path is a trip through a graph which visits each node exactly once. A graph may have multiple Hamiltonian Paths, only one, or even none. Given a graph, a starting point, and an endpoint, is there a Hamiltonian path?
We solve our problem by transforming E. coli cells with specially engineered plasmids.
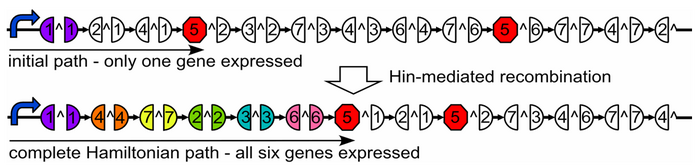
Designing a Plasmid
Our plasmid consists of reporter genes and HixC sites. HixC sites are placed within the coding regions of our reporter genes. The reporter genes are joined in such a way as to represent a graph. Each reporter gene represents a node, and the connection of two reporter genes together without any HixC sites in between represents an edge.