Difference between revisions of "Degradation of Xenobiotics by Halomicrobium mukohataei (Megan Reilly)"
(→Styrene degradation) |
(→Styrene degradation) |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
(BLAST of the gene of <i>H. mukohataei</i> obtained from RAST.<br> | (BLAST of the gene of <i>H. mukohataei</i> obtained from RAST.<br> | ||
[[Image:Sty3.png]] | [[Image:Sty3.png]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Gene 3.7.1.9 - hydroxymuconate:</b><br> | ||
| + | (BLAST of the gene of <i>Halogeometricium borinquese</i>. Sequence obtained from RAST.<br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Sty4.png]] | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
Revision as of 14:55, 1 October 2009
KEGG pathways that I have found viable genes for in the H. mukohataei genome:
- Benzoate degradation via hydroxylation
- Styrene degradation
- Caprolactam degradation
Possibly others, but either the gaps in other pathways are due to H. mukohataei possessing an alternate gene rather than one that is already known to exist in other genomes, or that a gene has not been identified in any genomes at all and requires wet-lab experiments to determine the sequence of the gene. These unknown genes must exist in several organisms, because the protein that they produce has been identified.
Contents
Benzoate degradation via hydroxylation
Click here to see the KEGG Pathway
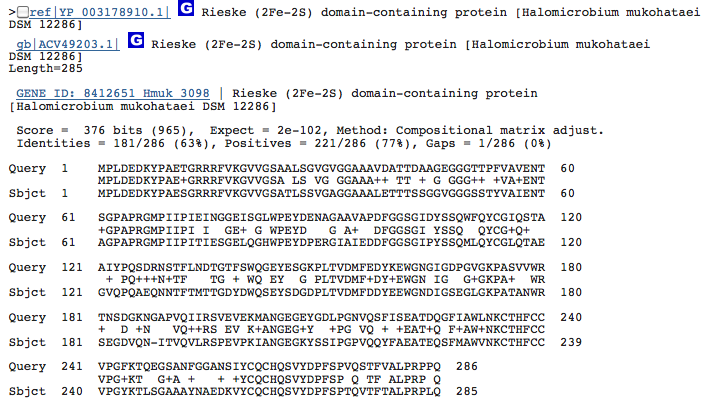
Gene 1.14.12.10 - Rieske (2Fe-2S) domain-containing protein:
(BLAST of H. marismortui; sequence of both microbes obtained from RAST.)
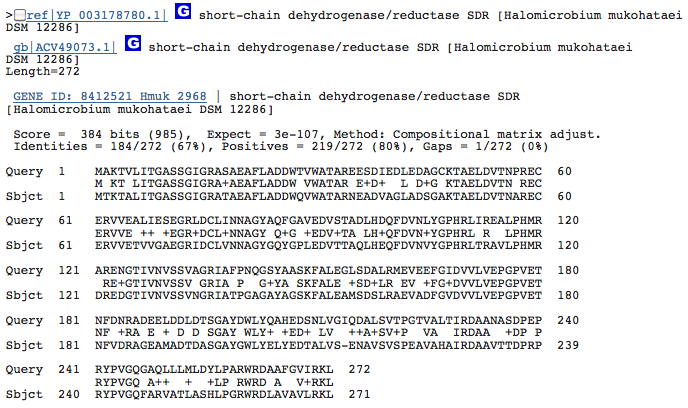
Gene 1.3.1.25 - putatative dehydrogenase
(BLAST of H. marismortui; sequence of both microbes obtained from RAST.)
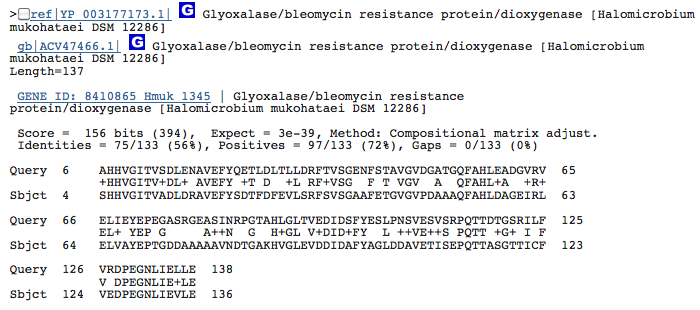
Gene 1.13.11.1 - putatative dioxygenase
(BLAST of H. marismortui; sequence of both microbes obtained from RAST.)
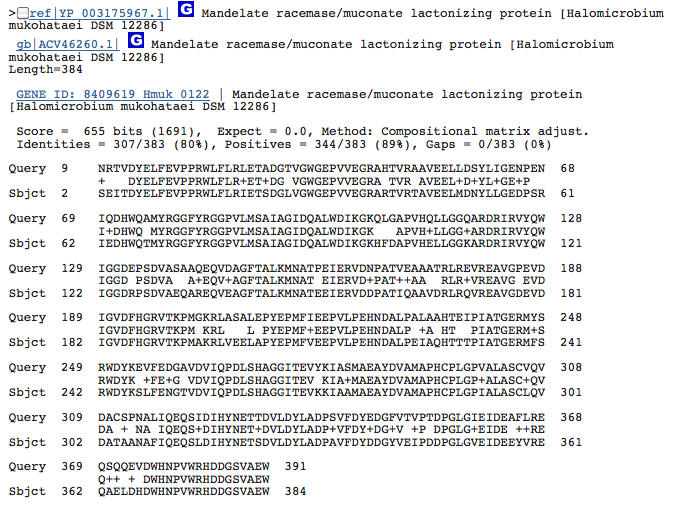
Gene 5.5.1.1 - muconate lactonizing protein
(BLAST of H. marismortui; sequence obtained from BRENDA.)
Gene 5.3.3.4 - putatative muconolactone D-isomerase
(BLAST of H. marismortui; sequences obtained from RAST.)
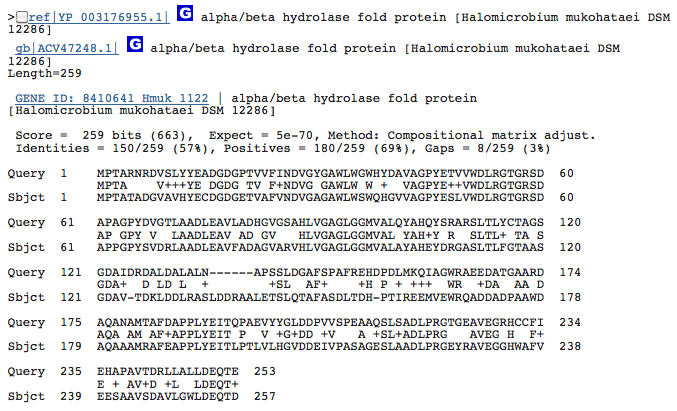
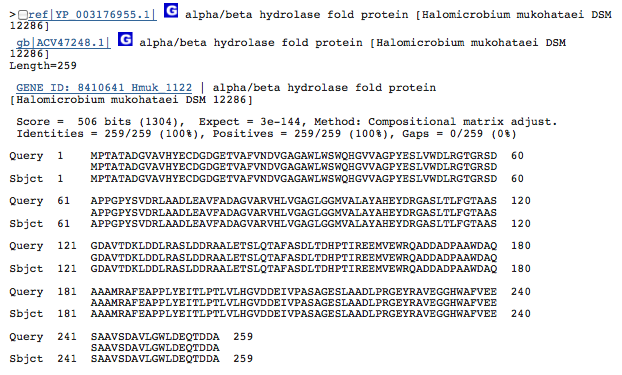
Gene 3.1.1.24 - predicted hydrolase or acyltransferase of alpha/beta superfamily
(Gene obtained from JGI, verified with BLAST.)
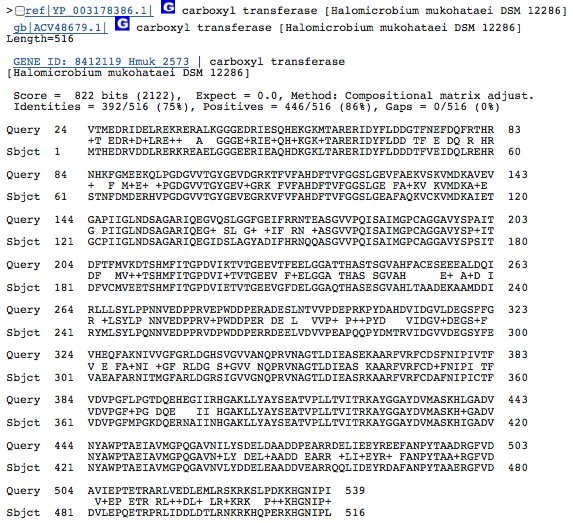
Gene 2.8.3.6 - carboxyl transferase
(BLAST of H. borinquense; sequences obtained from RAST.)
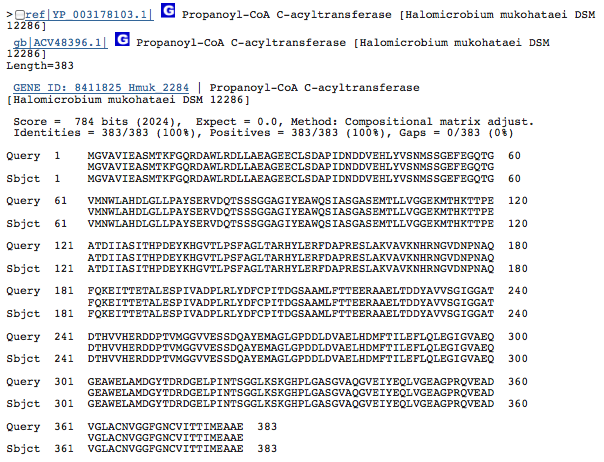
Gene 2.83.1.16 - acetyl CoA transferase
(Gene obtained from JGI, verified with BLAST.)
Styrene degradation
Click here to see the KEGG pathway.
Gene 1.13.11._ - aromatic compound dioxygenase:
(BLAST of H. marismortui compared to that of H. mukohataei. This gene is either not very well characterized or not conserved in archaea, as seen by the variation in predicted genes on JGI.)
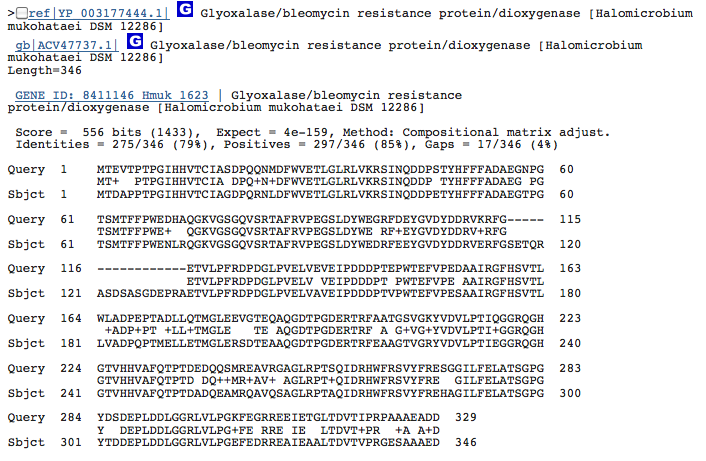
Gene 1.3.1.19 - putative dehydrogenase:
(BLAST of H. utahensis compared to that of H. mukohataei. This gene is not well characterized in archaea - the sequence of Pseudomonas putida was obtained from BRENDA.)
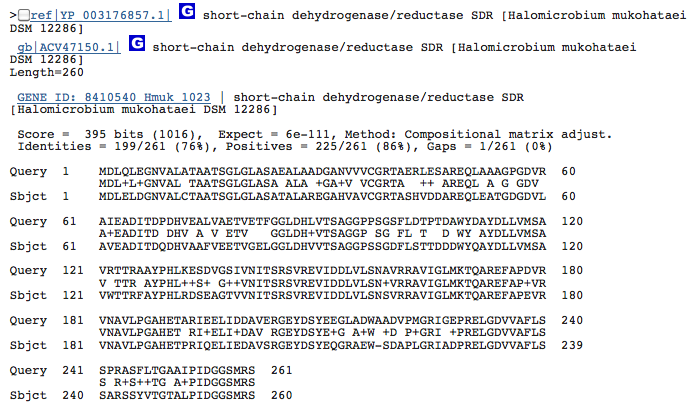
Gene 1.13.11.2 - catechol dioxygenase:
(BLAST of the gene of H. mukohataei obtained from RAST.

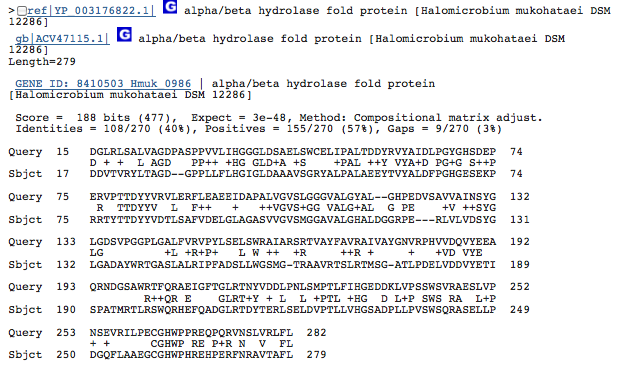
Gene 3.7.1.9 - hydroxymuconate:
(BLAST of the gene of Halogeometricium borinquese. Sequence obtained from RAST.
Caprolactam degradation
Click here to see the KEGG pathway.
Other potential biodegradable xenobiotics
Benzene, a low molecular weight petroleum hydrocarbon, has been shown to be utilized by an unnamed halophile as its sole source of energy. This organism was also able to degrade toluene, another aromatic hydrocarbon.Fathepure 2006
Phenol is a toxic, aromatic, white crystalline solid. It has been shown to be used as a carbon and an energy source by Halobacillus campisalis.Peyton 2003