Difference between revisions of "Directed Evolution and Synthetic Biology - Hunter Stone"
(→The Directed Evolution Method) |
(→The Directed Evolution Method) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==The Directed Evolution Method== | ==The Directed Evolution Method== | ||
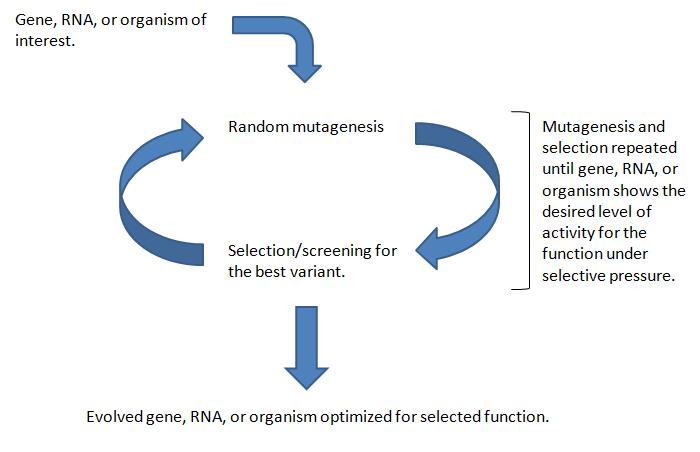
| − | Directed evolution is a method used to create a more efficient mutant of an existing gene, RNA, pathway or cell. | + | Directed evolution is a method used to create a more efficient mutant of an existing gene, RNA, pathway or cell. The method follows these general steps: |
| + | 1. A library of variants of the targeted construct (e.g. a gene, a cell, etc.) is generated through random changes of its genomic DNA. Methods of genetic randomization include error-prone PCR, mutagenic agents like Mutazyme, or random transposon integration. | ||
| + | 2. The variant library goes through a process of screening or selection to reveal the most productive members of the library. Selection and screening techniques are specific to desired function of each experiment (e.g. higher enzyme efficiency, greater cell resistance to ethanol). | ||
| + | 3. The most productive variant is resubmitted to the genetic randomization and selection processes. | ||
| + | 4. Steps 1-3 are repeated until the desired result is received - an evolved mutant more adept at the processes it was selected for than its unevolved parent. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:DIRECTEDEVOLUTION.jpg]] | [[Image:DIRECTEDEVOLUTION.jpg]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The power of directed evolution comes from two sources: its nonbiased nature and its capability of probing regions of the cell currently undescribed or beyond the present capabilities of linear modeling and reasoning. | The power of directed evolution comes from two sources: its nonbiased nature and its capability of probing regions of the cell currently undescribed or beyond the present capabilities of linear modeling and reasoning. | ||
Revision as of 16:25, 5 December 2007
Contents
Project Proposal
My project focuses on the use of random mutations to optimize synthetic pathways. Mathematical modeling of synthetic pathways is a powerful, proven tool to maximize product output. However, recently a series of unbiased strategies using recombinant methods have been shown to further increase product yield. These methods, which has been referred to as directed evolution, have produced powerful new methods and approaches for the synthetic biologist.
Introduction - Optimization and Directed Evolution
Researcher Jay Keasling has recently described a genetically-modified yeast strain that produces artemisinic acid, a chemical precursor to the antimalarial drug artemisinin. In these experiments, his team engineered yeast cells to express enzymes in a pathway that converts farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), a metabolic intermediate naturally occurring in yeast, into the desired product. Initially, however, this yeast strain was unable to produce any appreciable amount of artemisin. Keasling’s team had run into a key problem facing many projects in synthetic biology: optimization. Although we are increasingly able to build sophisticated constructs within living cells, the existence of these frameworks does not always correspond with the ability to fulfill their intended purposes efficiently and effectively.
Keasling’s team chose to address this problem by rationally modifying the metabolism of their yeast strain. Although they were successful in increasing desired product yields, the authors note that further optimization is necessary to meet their goals for cost of production. When one considers the work facing the group in the future, many questions arise. Were the changes they have already made to the yeast’s metabolism truly the best for optimizing artemisinin output? Could changes in other distantly-related metabolic pathways have also helped to increase yields? Are there presently unknown elements in the cell affecting the new pathway which could potentially be changed? Are the enzymes in the new pathway themselves working at maximum efficiency?
One technique with the potential to answer all of these questions is directed evolution.
The Directed Evolution Method
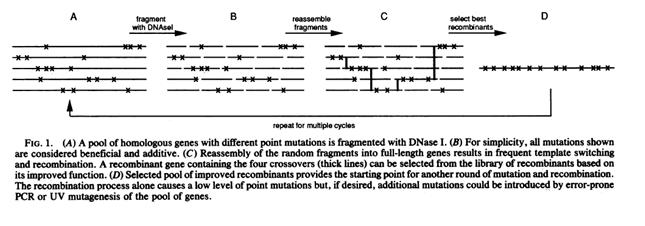
Directed evolution is a method used to create a more efficient mutant of an existing gene, RNA, pathway or cell. The method follows these general steps: 1. A library of variants of the targeted construct (e.g. a gene, a cell, etc.) is generated through random changes of its genomic DNA. Methods of genetic randomization include error-prone PCR, mutagenic agents like Mutazyme, or random transposon integration. 2. The variant library goes through a process of screening or selection to reveal the most productive members of the library. Selection and screening techniques are specific to desired function of each experiment (e.g. higher enzyme efficiency, greater cell resistance to ethanol). 3. The most productive variant is resubmitted to the genetic randomization and selection processes. 4. Steps 1-3 are repeated until the desired result is received - an evolved mutant more adept at the processes it was selected for than its unevolved parent.
The power of directed evolution comes from two sources: its nonbiased nature and its capability of probing regions of the cell currently undescribed or beyond the present capabilities of linear modeling and reasoning.
For a retrospective review directed evolution, click here.
Proof of Concept: Directed Evolution vs. Rational Modeling in Lycopene-producing E. coli
Researchers Hal Alper, Kohei Miyaoku and Greg Stephanopoulos have recently shown the effectiveness of using directed evolution for optimizing a synthetic construct. Previously, the researchers had engineered a strain of E. coli capable of synthesizing lycopene, a carotenoid naturally which naturally occurs in tomatoes but has more recently been incorporated in vitamin tablets for its antioxidant capabilities. The group was interested in further optimizing the lycopene output of this strain. Using computer modeling, they identified a series of gene knockouts sites which were predicted to increase the lycopene production. However, strains engineered with these knockouts were still unable to produced lycopene at the predicted “stoichiometric maximum.” This finding led the researchers to hypothesize that lycopene production was “limited by unknown kinetic or regulatory factors unaccounted for in the stoichiometric models.”
The researchers used directed evolution to find gene knockouts which might affect these unexplored regions of the cell. Random gene knockout was achieved using genome-wide integrating transposable elements (LINK). The random knockout strains were then tested through plating, which revealed increases in lycopene production efficiency as increases in red colony color. These tests revealed three gene knockout sites. All three knockout sites were different from the seven predicted by their models and two interrupted previously-undescribed genes which the researchers believe encoded proteins.
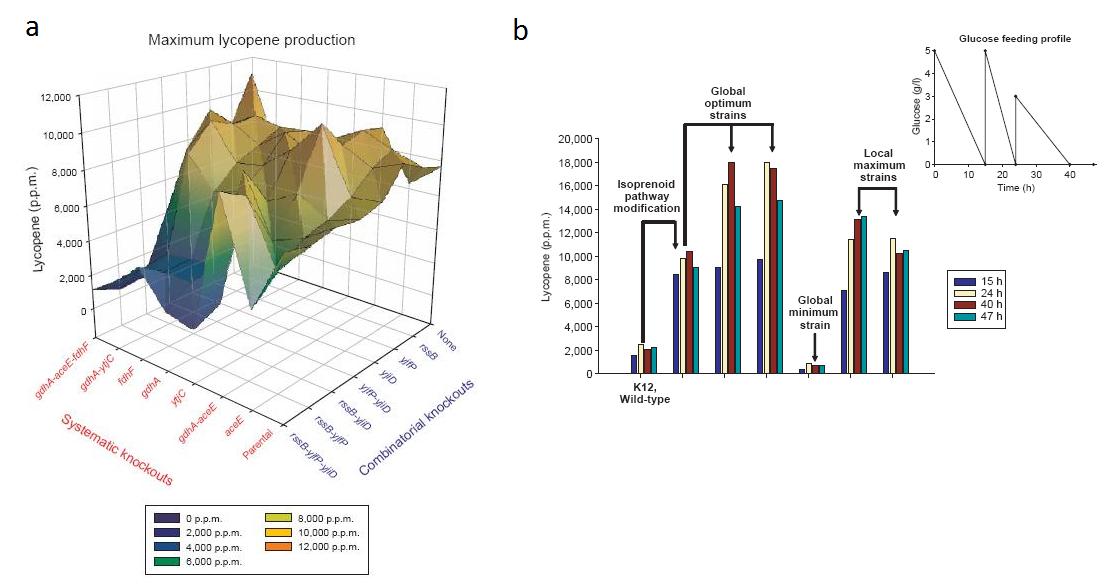
Next, the researchers were interested in determining to see how effective these three gene knockouts were at increasing lycopene production when compared to the knockouts they had predicting with computer modeling. To answer this question, the researchers created 64 unique strains of the lycopene-producing E. coli representing all possible combinations of the three knockouts selected by directed evolution, the seven model-predicted knockouts, and the two parental strains from which the “evolved” and model-predicted strains were derived. Lycopene production of the 64 strains was measured by extracting the lycopene from the each colony after and defined time and quantifying lycopene level by absorbance spectroscopy at 475. Of the two global maxima of this experiment, one had a knockout selected through directed evolution testing (Fig. 1a). Furthermore, this particular knockout strain also showed an earlier peak in lycopene production and when compared to the completely systematically-predicted knockout strain in batch fed culture (Fig. 1b).
(Alper, 2005 - Permission Pending)
Figure 1: The two measurements lycopene production in knockout strains of lycopene producing bacteria. (a) A landscape displaying the 64 strains resulting for all possible combinations of gene knockouts selected through systematic modeling and directed evolution (combinatorial knockouts). Lycopene production for each strain was measured at the end of a 48-h shake-flask fermentation and amount of lycopene produced was quantified through extraction form the cell pellet with acetone and supernatant absorbance at 475 nm. Of interest is global maximum strain ΔgdhA ΔaceE ΔPyjiD, which contains a knockout of the ΔPyjiD gene selected through directed evolution testing. (b) Lycopene production of the best knockout strains in batch-fed culture. From left to right, the K12 strain from which combinatorial mutants were derived, the preengineered parental strain from which the systematically-selected knockout strains were derived, global maximum strain ΔgdhA ΔaceE ΔfdhF, global maximum strain ΔgdhA ΔaceE ΔPyjiD, and the global minimum strain and two local maximum strains from landscape 1a. Of interest is knockout strain ΔgdhA ΔaceE ΔPyjiD (fourth from the left). This strain, which has a gene knockout selected through directed evolution testing, shows the same maximum in lycopene productivity as the entirely systematically-predicted strain ΔgdhA ΔaceE ΔfdhF (third from left), but also shows an earlier peak in this productivity and more sustained lycopene production.
Weaknesses of the Method
Although the method of directed evolution is promising to synthetic biology, there are some key weaknesses to this technique. The process of genetic randomization and selection can take long periods of time depending on the construct being used or the trait being selected for. Using slow-growing bacterium or trying to evolve production of compounds that accumulate very slowly can add months to the process. In addition, directed evolution does not always produce evolved mutants significantly more adept at selected functions than their parents. Selective pressure can be difficult to increase in selection tests; in addition, false positives can slip through screening and selection while beneficial mutations can be lost due to the adverse affects they have on the organism unrelated to the function of interest.
Increases in Sophistication
Although the concerns addressed in the previous section are very real, new methods of directed evolution have been developed to address these problems and make directed evolution an even more effective process. The following papers describe three new methods for directed evolution aiming to increase the efficiency of the process in different ways.
Semi-Synthetic DNA Shuffling and Doramectin
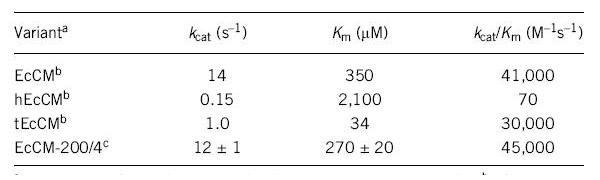
A Simple Method for Highly Evolved Enzymes
Global Transcriptome Machinery Engineering
From these papers, we see that directed evolution is a method which has become increasingly modular with different methods of the process that can be employed depending on the nuances of the studied construct.
Conclusion
Figure Bank
Neuenschwander, M., M. Butz, C. Heintz & D. Hilvert. 2007. A simple selection strategy for evolving highly efficient enzymes. Nature Biotechnology 25(10): 1145-1147.
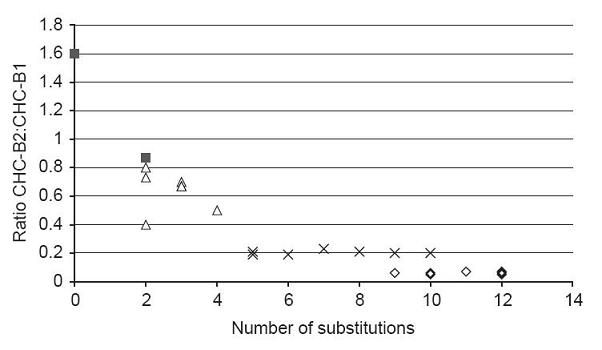
(Neuenschwander, 2007 - Permission Pending)
Stutzman-Engwall, K., S. Conlon, R. Fedechko, H. McArthur, K. Pekrun, Y. Chen, S. Jenne, C. La, N. Trinh, S. Kim, Y. Zhang, R. Fox, C. Gustafsson & A. Krebber. 2005. Semi-synthetic DNA shuffling of aveC leads to improved industrial scale production of doramectin by Streptomyces avermitilis. Metabolic Engineering 7: 27-37.
(Stemmer, 1994 - Permission Pending)
(Stutzman-Engwall, 2005 - Permission Pending)
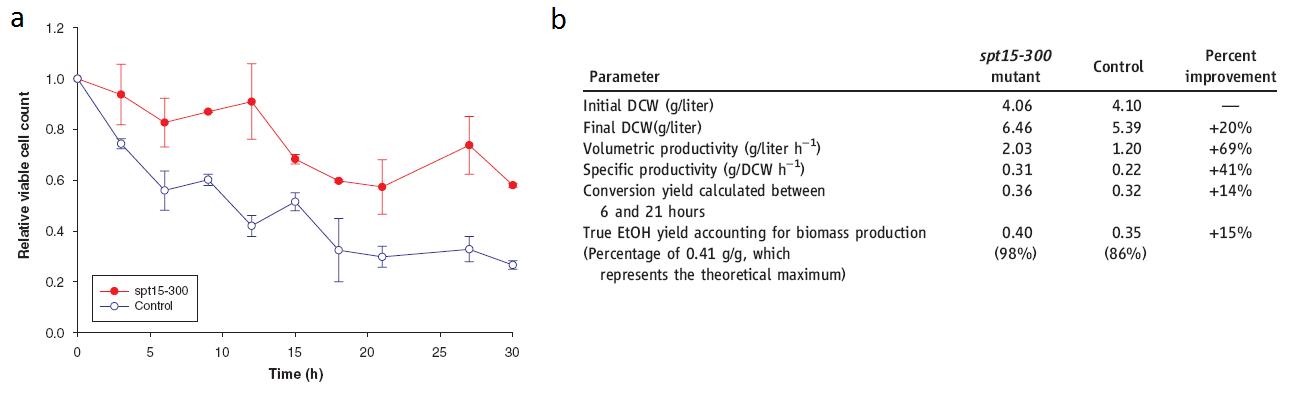
Alper, H., J. Moxley, E. Nevoigt, G.R. Fink & G. Stephanopoulos. 2006. Engineering yeast transcription machinery for improved ethanol tolerance and production. Science 314: 1565-1568.
(Alper, 2006 - Permission Pending)