Difference between revisions of "Disease resistance to fungal diseases"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[http://www.plantcell.org/content/20/2/241.full#ref-11 Explanation of Chitin Signaling and Fungal Invasion Response] | [http://www.plantcell.org/content/20/2/241.full#ref-11 Explanation of Chitin Signaling and Fungal Invasion Response] | ||
| − | -plants can recognize “surface-derived molecules” that elicit a general immune response (this is in addition to R gene-mediated pathways) | + | -plants can recognize “surface-derived molecules” that elicit a general immune response (this is in addition to R gene-mediated pathways)<br> |
| − | + | –pathogen-associated or microbe-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs/MAMPs)<br> | |
| − | –pathogen-associated or microbe-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs/MAMPs) | + | -PAMPs are important for microbial invasion of a host cell<br> |
| − | + | -glucans, chitins, and proteins derived from fungal cell walls serve as elictors, or “pathogen derived molecules” ([https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache:roR2_eWr0IkJ:iibce.edu.uy/cursopedeciba/seminarios%2520y%2520material%2520de%2520apoyo/2003_Montesano_Brader_Palva.pdf+elicitor+of+plant+response&hl=en&gl=us&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEESijnBFewyWFCmTd7Uu7_ItmGcc08uxEO-1BZ1cEusmypDaAwjPkQtm4jqcJKacRaajhkQgJFQ3UsdeZhJPlkyDUyd7Vg5RLHfqcqkaBcTINdi8FKJpQCihlyMx3DluToDLRRPrM&sig=AHIEtbQhHsg-pLXH8Hzr_9HmiVg2PVe9fA Montesano et al 2003])<br> | |
| − | -PAMPs are important for microbial invasion of a host cell | + | -during fungal infection, chitinases in the infected cell degrade the chitin on the cell wall of the invading fungus<br> |
| − | + | -the remaining chitin fragments (chitooligosaccarides) then also serve as elicitors that provoke necessary “defense response genes”<br> | |
| − | -glucans, chitins, and proteins derived from fungal cell walls serve as elictors, or “pathogen derived molecules” ([https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache:roR2_eWr0IkJ:iibce.edu.uy/cursopedeciba/seminarios%2520y%2520material%2520de%2520apoyo/2003_Montesano_Brader_Palva.pdf+elicitor+of+plant+response&hl=en&gl=us&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEESijnBFewyWFCmTd7Uu7_ItmGcc08uxEO-1BZ1cEusmypDaAwjPkQtm4jqcJKacRaajhkQgJFQ3UsdeZhJPlkyDUyd7Vg5RLHfqcqkaBcTINdi8FKJpQCihlyMx3DluToDLRRPrM&sig=AHIEtbQhHsg-pLXH8Hzr_9HmiVg2PVe9fA Montesano et al 2003]) | + | -LysM RLKs (LsyM domain-containing receptor-like kinases): relatively large plant-specific protein family that researchers may suggest play a significant role in detecting fungal chitin<br> |
| − | |||
| − | -during fungal infection, chitinases in the infected cell degrade the chitin on the cell wall of the invading fungus | ||
| − | |||
| − | -the remaining chitin fragments (chitooligosaccarides) then also serve as elicitors that provoke necessary “defense response genes” | ||
| − | |||
| − | -LysM RLKs (LsyM domain-containing receptor-like kinases): relatively large plant-specific protein family that researchers may suggest play a significant role in detecting fungal chitin | ||
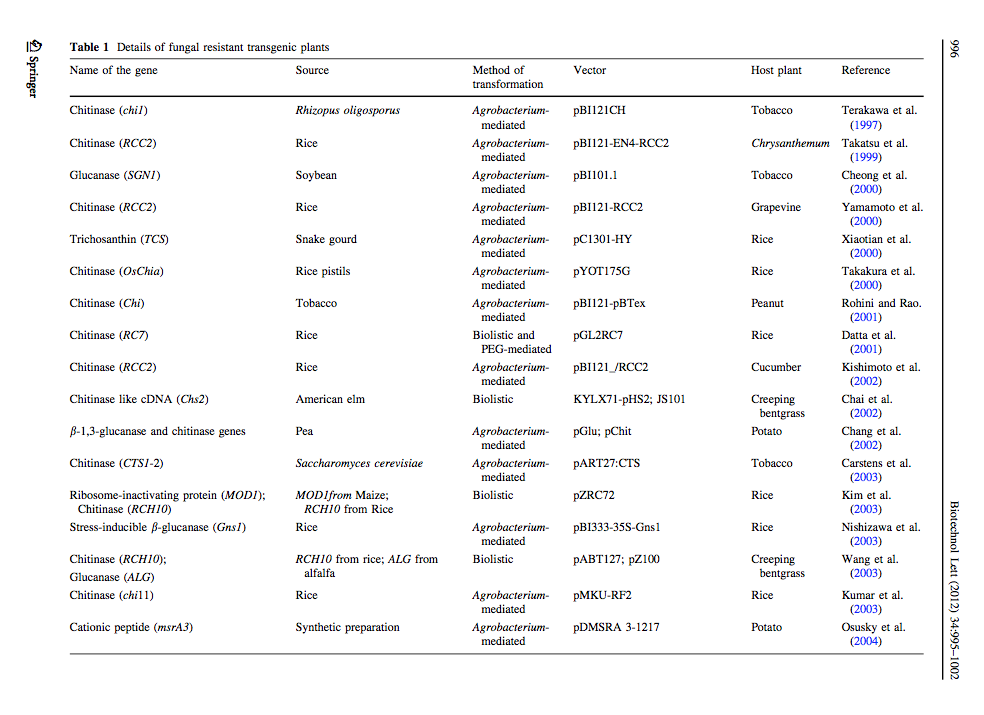
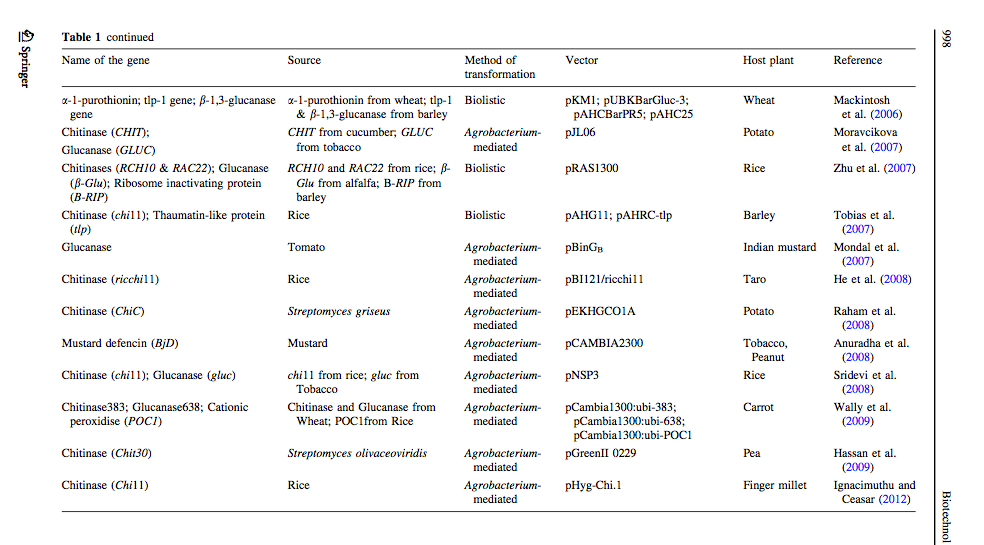
[http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10529-012-0871-1 Ceasar & Ignacimuthu 2012] identified genes (mainly chitinases and glucanases) used into genetic engineering of crop plants. The tables below list important list the genes transformed and their source organism. | [http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10529-012-0871-1 Ceasar & Ignacimuthu 2012] identified genes (mainly chitinases and glucanases) used into genetic engineering of crop plants. The tables below list important list the genes transformed and their source organism. | ||
Revision as of 18:57, 19 February 2013
Media:Potential_Genes_of_Interest.xlsx
Background on Resistance (R) genes and avirulence (Avr) genes (Hammond-Kosack & Jones 1997)
R genes are found in the plant, while corresponding Avr gene is in the pathogen
Presumed roles of R genes:
- help plants detect pathogenic Avr gene products
- initiate signal transduction pathways that will help defend against the pathogen
- "have the capacity to evolve new R gene specificities rapidly"
If the R gene or corresponding pathogenic Avr gene are not present or altered, then plant is infected with the disease
The R protein recognizes the Avr gene product (ligand), activating a signal transduction cascade that initiates the defense against the pathogen. Thus, the R gene is turned on in healthy plants. R proteins must be able to evolve quickly in order to target new pathogens specifically. The evolution of the Avr genes directly impacts the evolution of the related R gene (coevolution).
Explanation of Chitin Signaling and Fungal Invasion Response
-plants can recognize “surface-derived molecules” that elicit a general immune response (this is in addition to R gene-mediated pathways)
–pathogen-associated or microbe-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs/MAMPs)
-PAMPs are important for microbial invasion of a host cell
-glucans, chitins, and proteins derived from fungal cell walls serve as elictors, or “pathogen derived molecules” (Montesano et al 2003)
-during fungal infection, chitinases in the infected cell degrade the chitin on the cell wall of the invading fungus
-the remaining chitin fragments (chitooligosaccarides) then also serve as elicitors that provoke necessary “defense response genes”
-LysM RLKs (LsyM domain-containing receptor-like kinases): relatively large plant-specific protein family that researchers may suggest play a significant role in detecting fungal chitin
Ceasar & Ignacimuthu 2012 identified genes (mainly chitinases and glucanases) used into genetic engineering of crop plants. The tables below list important list the genes transformed and their source organism.
<center?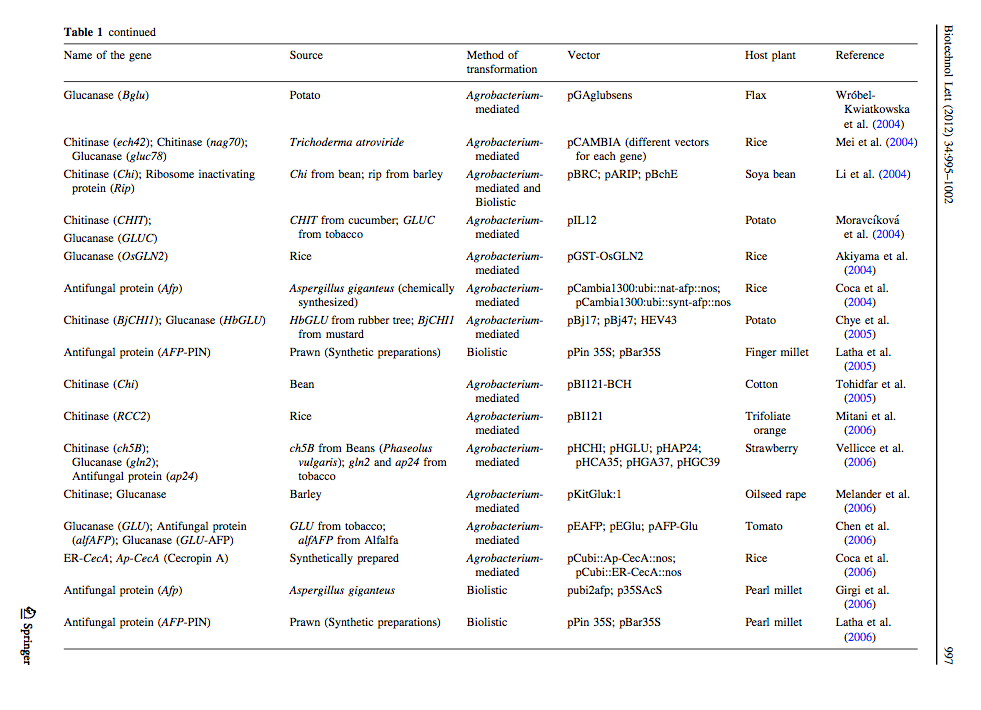
3 Common Blueberry Fruit Rots: ([ohioline.osu.edu/hyg-fact/3000/pdf/3213.pdf OSU])
- Alternaria - postharvest rot; most common
Caused by Alternaria tenuissima
- Anthracnose - serious pre- and postharvest disease
Caused by Colletotrichum acutatum (Yoshida et al. 2007)
- Botrytis - normally minor, but can be severe
Caused by Botrytis cinerea
Things to Look Up:
abscisic acid?
KEGG Pathway - environmental information processing - signal transduction - plant hormone transduction
(look at dormancy)