Difference between revisions of "Disease resistance to fungal diseases"
(→Colletotrichum) |
|||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
KEGG Pathway - environmental information processing - signal transduction - plant hormone transduction | KEGG Pathway - environmental information processing - signal transduction - plant hormone transduction | ||
(look at dormancy) | (look at dormancy) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00798.x/full Differential expression of strawberry genes as a result of ''Colletotrichum'' expression] | ||
Revision as of 19:54, 19 February 2013
Media:Potential_Genes_of_Interest.xlsx
Contents
Background on Resistance (R) genes and avirulence (Avr) genes
R genes are found in the plant, while corresponding Avr gene is in the pathogen
Presumed roles of R genes:
- help plants detect pathogenic Avr gene products
- initiate signal transduction pathways that will help defend against the pathogen
- "have the capacity to evolve new R gene specificities rapidly"
If the R gene or corresponding pathogenic Avr gene are not present or altered, then plant is infected with the disease
The R protein recognizes the Avr gene product (ligand), activating a signal transduction cascade that initiates the defense against the pathogen. Thus, the R gene is turned on in healthy plants. R proteins must be able to evolve quickly in order to target new pathogens specifically. The evolution of the Avr genes directly impacts the evolution of the related R gene (coevolution).
3 Common Blueberry Fruit Rots
[ohioline.osu.edu/hyg-fact/3000/pdf/3213.pdf OSU
- Alternaria - postharvest rot; most common
Caused by Alternaria tenuissima
- Anthracnose - serious pre- and postharvest disease
Caused by Colletotrichum acutatum (Yoshida et al. 2007)
- Botrytis - normally minor, but can be severe
Caused by Botrytis cinerea (genomic analysis of Botrytis, a necrotrophic fungus)
General Information & Genes
Explanation of Chitin Signaling and Fungal Invasion Response
-plants can recognize “surface-derived molecules” that elicit a general immune response (this is in addition to R gene-mediated pathways)
–pathogen-associated or microbe-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs/MAMPs)
-PAMPs are important for microbial invasion of a host cell
-glucans, chitins, and proteins derived from fungal cell walls serve as elictors, or “pathogen derived molecules” (Montesano et al 2003)
-during fungal infection, chitinases in the infected cell degrade the chitin on the cell wall of the invading fungus
-the remaining chitin fragments (chitooligosaccarides) then also serve as elicitors that provoke necessary “defense response genes”
-LysM RLKs (LsyM domain-containing receptor-like kinases): relatively large plant-specific protein family that researchers may suggest play a significant role in detecting fungal chitin
Ceasar & Ignacimuthu 2012 identified genes (mainly chitinases and glucanases) used into genetic engineering of crop plants. The tables below list important list the genes transformed and their source organism.
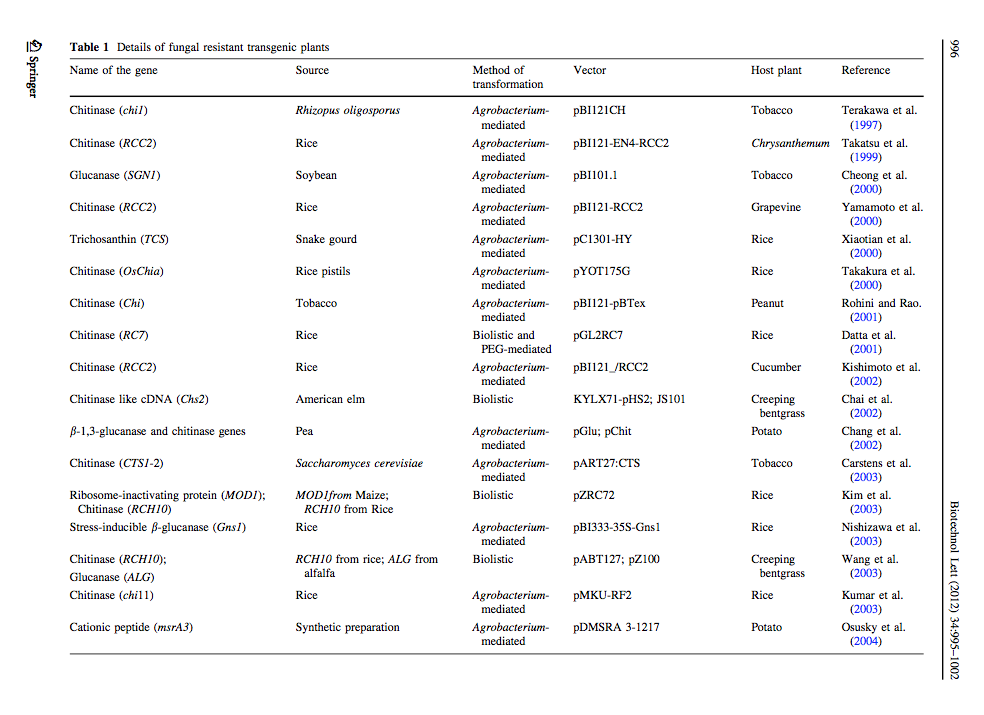
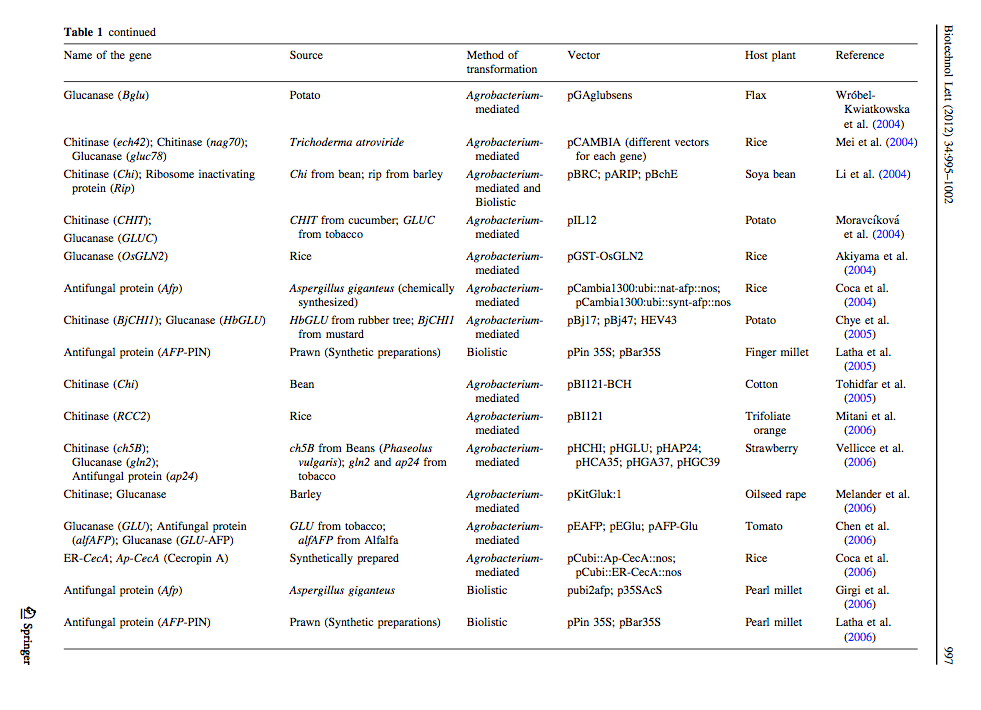
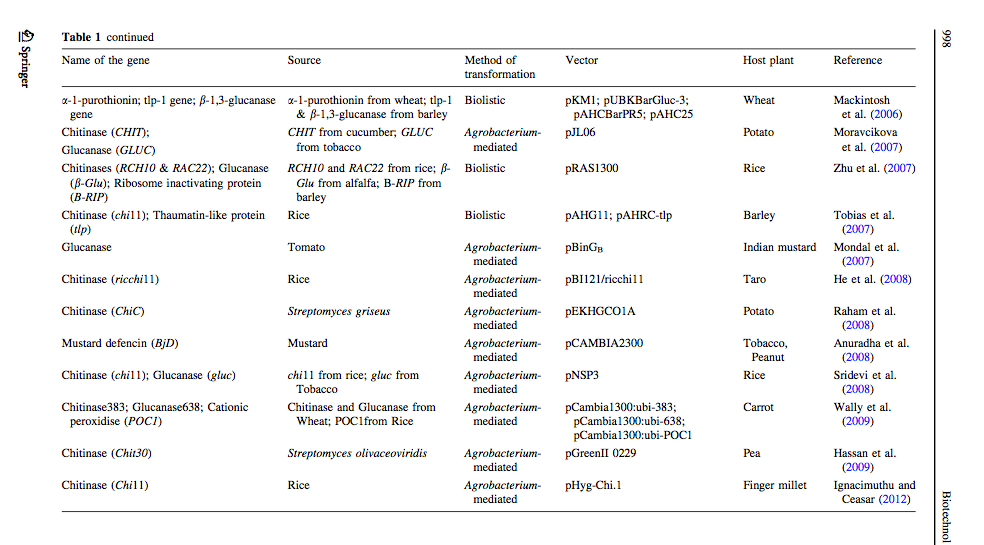
Alternaria
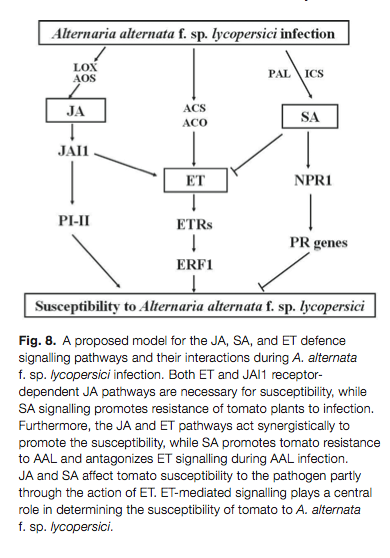
Jia et al. 2013 discusses the role of 3 plant hormones (ethlynene [ET], jasmonic acid [JA], and salicylic acid [SA]) in necrotrophic fungal infections (such as Alternaria alternata) in the tomato. They ultimately suggest the following pathway:
Colletotrichum
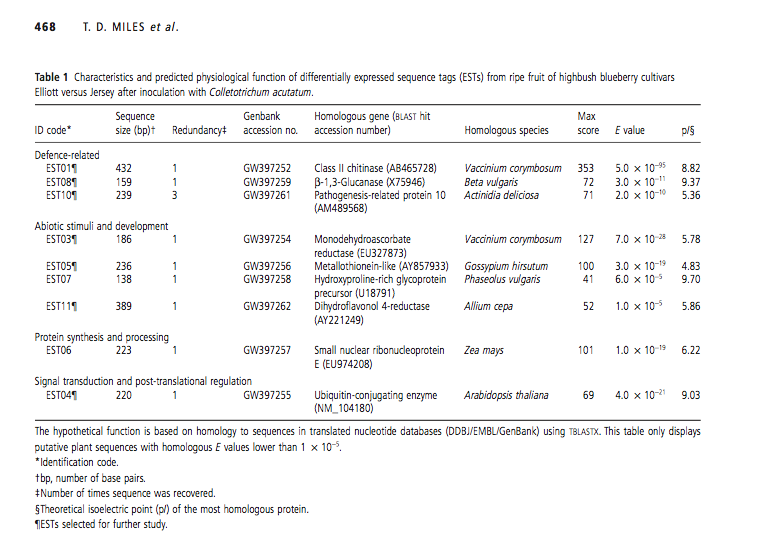
Miles et al. 2011 identified ESTs in a Colletotrichum-resistant blueberry strains that were highly homologous to known defense genes, including a class II chitinase, pathogenesis-related protein 10 (PR10), and β-1,3-glucanase. They also found ESTs, such as monodehydroascorbate reduc- tase (EST03) and a metallothionein-like protein (EST05), associated with oxidative stress, which helps protect the plant from oxidative damage.
Things to Look Up
abscisic acid?
KEGG Pathway - environmental information processing - signal transduction - plant hormone transduction
(look at dormancy)
Differential expression of strawberry genes as a result of Colletotrichum expression