Difference between revisions of "Katie's Assignment"
Karicheson (talk | contribs) |
Karicheson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
[[Image:hcmecw.jpg]] | [[Image:hcmecw.jpg]] | ||
| − | Aspartate | + | Aspartate Carbamoyltransferase Sequences: (Query= our species' and Subject=''H. salinarium'' aspartate carbamoyltranserase enzyme protein sequence) |
[[Image:hcac.jpg]] | [[Image:hcac.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 22:08, 30 September 2009
I am interested in exploring the genetic make up of enzymes that have been previously identified as being "salt dependent" for activity- such as citrate synthase, malic enzyme and aspartae transcarbamylase (which are all found in our species' genome).
What is citrate synthase and what is its role in our species?
What is malic enzyme (malate dehydrogenase) and what is its role in our species?
Why/How did I pick these three enzymes?
JGI Genes:
Citrate Synthase JGI: 2916896..2918032 (+) (1137bp). . . nucleotide sequence
Allosteric NADP-dependent Malic Enzyme 2055313..2057565 (+) (2253bp) . . . nucleotide sequence
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase regulatory subunit: 1503175..1503639 (-) (465bp). . . sequence
carbamoyltransferase: 1503636..1504550 (-) (915bp) . . . sequence
RAST Genes:
Citrate Synthase TCA Cycle. . . sequence . . . protein sequence
>fig|485914.5.peg.3029 [Halomicrobium mukohataei DSM 12286] [Citrate synthase (si) (EC 2.3.3.1)] MSDDLKQGLEGVLVTESELSKIDGDAGKLVYRGYTIEDLATGASFEEVLY LLWHGHLPNAAELDEFTDAMVEERHVDDDVMQTVEQLADADENPMAALRT AVSMLSSHDPDAETDPTDLDANLRKGRRITAKIPTVLAAFARFRDGQDAV EPREDLSHAANFLYMLNGEAPDEVLAETFDMALVLHADHGINASTFSAMV TASTLSDLHSAITSAIGTLKGSLHGGANQDVMEMLKEVDDAQQDPIDWVK TALDEGRRVSGFGHRVYNVKDPRAKILSQRSKELGEAAGSLKWYEMSTAI EDYLKAEKGLAPNVDFYSASTYYQMGIPIDIYTPIFAMSRVGGWTAHVLE QYENNRLIRPRARYVGPTDQTFVPLDER
Citrate Synthase Glyoxylate Synthesis . . . protein sequence
NADP-dependent malic enzyme. . . protein sequence
>fig|485914.5.peg.2113 [Halomicrobium mukohataei DSM 12286] [NADP-dependent malic enzyme (EC 1.1.1.40)] MGLDEDALDYHGRAPPGKIEIATTKPTNTQRDLSLAYSPGVAAPCEAIHE TPEDAFKYTARGNLVAVVSDGSAVLGLGDIGPEASKPVMEGKGVLFKRFA DIDVFDLELDTDDPDAMIEAVDAMGPTFGGINLEDIAAPACFEIERELRE RMDVPVFHDDQHGTAIISGAALLNAADIVDKELEEMEIVFSGAGASAIAS ARFYVSLGVRKENITMCDSSGIITADRVENDGLNRYKAEFASEGTGGDLA DALAGADAFVGLSVGGVVDEAMVRSMASEPIIFAMANPDPEIDYETAKAA RDDTVIMATGRSDYPNQVNNVLGFPFIFRGALDVRATEINEEMKVAAARA LARLARQDVPDAVVKAYGDQPLQFGPEYIIPKPLDPRVLFEVTPAVAEAA MDSGAARKSIDLDDYVERLEARLGKSREMMRVVLNKAKSDPKRVVLAEGD DEKMIRAAYQLIEQGIAEPVLLGDRDRISAITDTLGLAFEPEIVDPDEGG LDEYADRLYELRQRKGVTRREADELVTDGNYLGSVMVEMGDADAMLTGLT HHYPSALRPPLQIVGTAPEAEYAAGVYMLTFRNRVVFCADTTVNTDPDAD VLTEVTRHTAELARRFNVEPRAAMLSYSNFGSVDSPSTRAPRRAAERLRE DPATDFPVDGEMQADTAVVEDILQGTYEFSELDDPANVLVFPSLEAGNIG YKLLQRLGGAEAIGPMLVGMDKPVHVLQRGDEVKDIVNMAGVAVVDAQDD
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase
>fig|485914.5.peg.1562 [Halomicrobium mukohataei DSM 12286] [Aspartate carbamoyltransferase (EC 2.1.3.2)] MRQDHIISAKQLSRRDIEAVLDRAAEIAADPSAYADRHEGSLLGLLFFEP STRTKMSFSAAMKRLGGDIVDMGTVESSSVKKGESLADTVRVVEGYADAL VLRHPSEGAAQMASEFVDAPLINAGDGAGQHPTQTLLDLYTIRENAGFDD LSIGIMGDLKYGRTVHSLAHALTVFDARQHFVSPESLQLPRSVRYDLHES GAEVREHTDLDDVLSELDVLYVTRIQKERFPDESEYHEVAGEYQIDAATI REHNEDLTVMHPLPRVDEIDHDVDELDGAQYFQQAHNGVPVRMALLDMVL EESR
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase regulatory chain
Main Tasks
1). Verify annotation of all genes from each annotation service: start and stop codon, SD sequence, are the genes different between the annotation services?
JGI Genes:
Citrate Synthase -50 downstream bases: (red= stop and start codons, green= downstream bases)
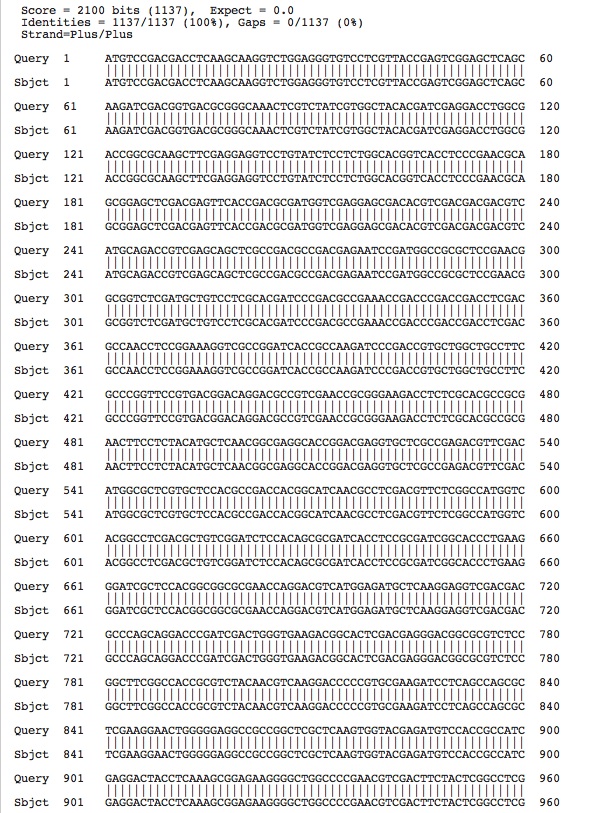
The two citrate synthase genes annotated from RAST are the same gene. . . below are the nucleotide blast alignment results:

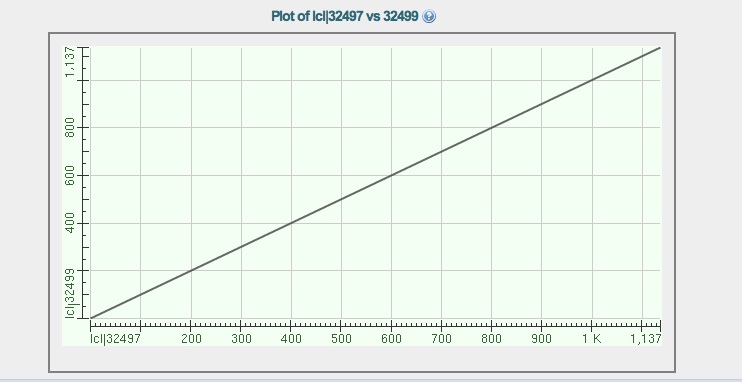
The citrate synthase gene from JGI matches the citrate synthase genes from RAST, nucleotide blast alignment dot plot is below:
The aspartate carbamoyltransferase regulatory gene sequences are a 100% match between the two annotation services.
The aspartate carbamoyltransferase gene sequences are the same between both annotation services as well.
The malic enzyme genes are 100% the same between the two annotation services as well.
I also checked to see if the aspartate carbamoyltransferase regulatory subunit was part of the aspartate carbamoyltransferase gene but it was not as confirmed by blastn with alignment and the nucleotide base regions where the gene occurs.
2). Look for other genes in our species' genome that are similar and may have been missed during annotation
Citrate Synthase blasted against our genome using Genome Portal: Two hits that are small but maybe a conserved region between the three enzymes that makes them salt dependent. Note that the subject alignments do not fall within any of the other two genes we are studying and thus this correlated sequence within our species' genome is not from one of the other salt dependent enzyme genes.
Malic Enzyme blasted against our species' genome using Genome Portal: Three hits shown below:

Aspartate carbamoyltransferase blasted against our species' genome using Genome Portal, results are below: (no hits besides the original gene)
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase regulatory unit blasted against out species' genome using Genome Portal, results are below: (no other hits besides the original gene)
3). Note the pathways and systems that these genes play a role in
4). Look at the sequences from the halophile studied in the article as compared to these gene sequences Lanyi in his paper, "Salt- Dependent Properties of Proteins from Extremely Halophilic Bacteria ," explores multiple enzymes that require salt to function properly. The three I have choosen to study: citrate synthase, malic enzyme and asparatate transcarbamylase, were isolated from H. cutirubrum. I had difficulty finding H. cutirubrum sequences in NCBI so I did some background research and discovered that H. cutirubrum is a specific strain of the H. salinarium species. According to Ventoso and Oren, there is no difference between this strain and the H. salinarium species.
The H. salinarium genome webpage outlines the three genes and below are the gene sequences:
Citrate Synthase . . . Protein Sequence and Information about the Protein
Malate Dehydrogenase (malic enzyme) . . .Protein Sequence and Information about the Protein
Aspartate Carbamoyltransferase . . . Protein Sequence and Information about Protein
Comparison of Each Enzyme's Protein Sequences using blastp and clustalW. . .
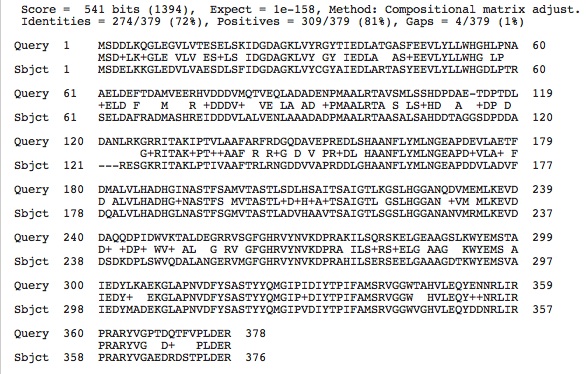
Citrate Synthase Sequences:
Malic Enzyme Sequences: (Query=our species' malic enzyme protein sequence and Subject= H. salinarium malic enzyme sequence)
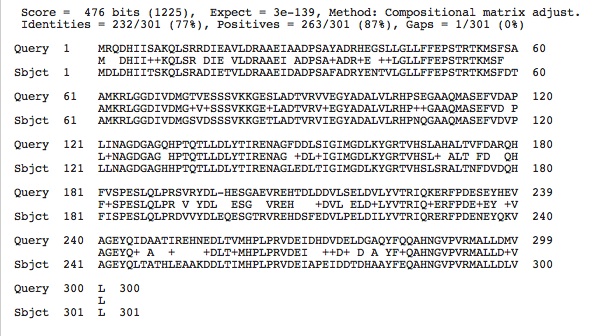
Aspartate Carbamoyltransferase Sequences: (Query= our species' and Subject=H. salinarium aspartate carbamoyltranserase enzyme protein sequence)
5). Find these genes in other halophiles in adopt a genome project and in the other 8 genomes of halophiles that have been annotated
6). Blast results of our species' genes: pick halophiles, bacteria, and eukarya to compare nucleotide sequence and protein sequence to (separate salt-loving and non-salt loving)
7). Look for differences in predicted protein structure and potential amino acid bias. (ClustalW)
8). Look for similarities between the genes for these 3 enzymes that are salt dependent.