Difference between revisions of "Determining whether genes called in JGI and RAST are identical"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
When working with multiple annotations, it is often useful to determine if a gene called by one annotation service is called by the other annotation service. The easiest way to determine if genes are called in both annotations is to compare start and stop codons. For large numbers of genes, Perl programs can be created to automate the process of comparing annotated genomes. However, if only a small number of genes are being compared, it can often be more efficient to compare start and stop codons manually. | When working with multiple annotations, it is often useful to determine if a gene called by one annotation service is called by the other annotation service. The easiest way to determine if genes are called in both annotations is to compare start and stop codons. For large numbers of genes, Perl programs can be created to automate the process of comparing annotated genomes. However, if only a small number of genes are being compared, it can often be more efficient to compare start and stop codons manually. | ||
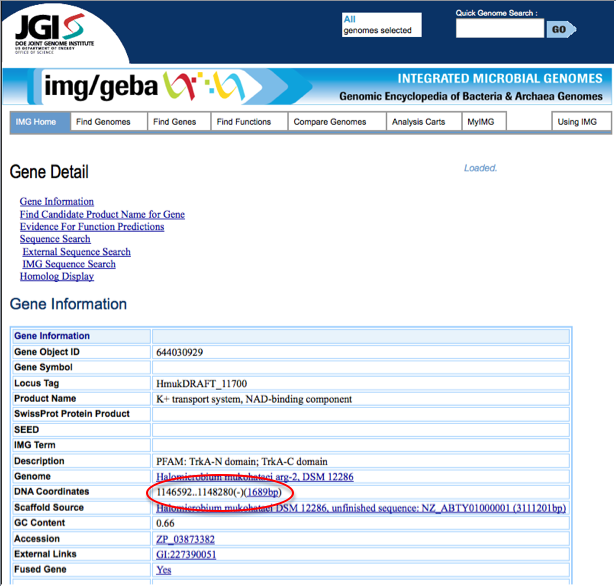
| − | To compare start and stop codons from JGI and RAST, first one must find the start and stop codons for the gene of interest. In JGI, start from the [[http://img.jgi.doe.gov/cgi-bin/geba/main.cgi?section=GeneDetail&page=geneDetail&gene_oid=644030929 Gene detail page]]. | + | To compare start and stop codons from JGI and RAST, first one must find the start and stop codons for the gene of interest. In JGI, start from the [[http://img.jgi.doe.gov/cgi-bin/geba/main.cgi?section=GeneDetail&page=geneDetail&gene_oid=644030929 Gene detail page]]. On this page, under '''Gene Information''', the start and stop codon are listed next to '''DNA coordinate'''. JGI also labels whether the gene is on the plus strand or minus strand of DNA. |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:JGI_circle.png]] | ||
Revision as of 01:21, 8 October 2009
When working with multiple annotations, it is often useful to determine if a gene called by one annotation service is called by the other annotation service. The easiest way to determine if genes are called in both annotations is to compare start and stop codons. For large numbers of genes, Perl programs can be created to automate the process of comparing annotated genomes. However, if only a small number of genes are being compared, it can often be more efficient to compare start and stop codons manually.
To compare start and stop codons from JGI and RAST, first one must find the start and stop codons for the gene of interest. In JGI, start from the [Gene detail page]. On this page, under Gene Information, the start and stop codon are listed next to DNA coordinate. JGI also labels whether the gene is on the plus strand or minus strand of DNA.