RRNA operon 2009
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the central component of the ribosome, the protein manufacturing machinery of all living cells. The function of the rRNA is to provide a mechanism for decoding mRNA into amino acids and to interact with the tRNAs during translation by providing peptidyl transferase activity.The tRNA then brings the necessary amino acids corresponding to the appropriate mRNA codon. Archaea contains either a single rDNA operon or multiple copies of the operon.
Archea usually contains three kinds of rRNA: 16S, 5S and 23S. 5S and 23S are part of the large ribosomal subunit, whereas 16S is part of the small robosomal unit and is responsible for recognizing the Shine-Delgarno sequences on most mRNAs. 16S is one of the most highly conserved sequences in any genome. 23S has peptidyl transferase activity and assists in binding adjacent amino acids during translation of an mRNA. Chloramphenicol acts by binding to the 23S rRNA so studying this gene in particular might explain why our species is chloramphenicol resistant.
All the suggested 5S rRNA genes in our genome were identical, as shown in the BLAST2 comparison here:
Typically in prokaryotes, rRNA genes are linked in transcription in the order of (5') 16s-23s-5s (3'). However, this only occurs at one instance in our genome.
Contents
- 1 5s rRNA (445..583(+); 1766895..1767033(-); 1962..2100(+)), all three consisted of 139 identical base pairs.
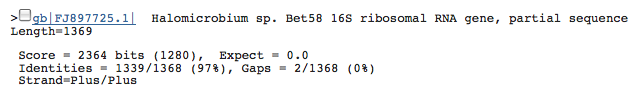
- 2 16s rRNA (1770405..1771883(-); 1479bp): Top three species with similar 16s rRNA sequences
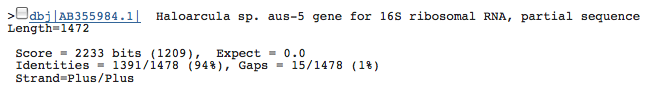
- 3 16s rRNA (3107428..3108907(+); 1480bp): Top three species with similar 16s rRNA sequences
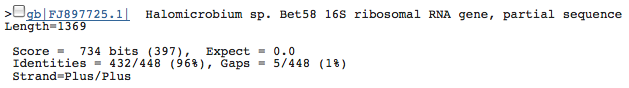
- 4 16s rRNA (218960..219414(+); 455bp): Top three species with similar 16s rRNA sequences
- 5 23S rRNA
- 6 23S rRNA
- 7 23S rRNA
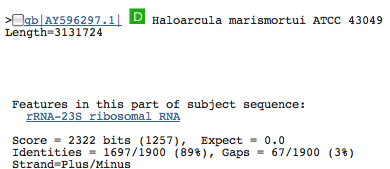
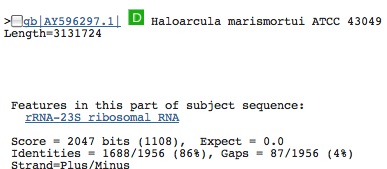
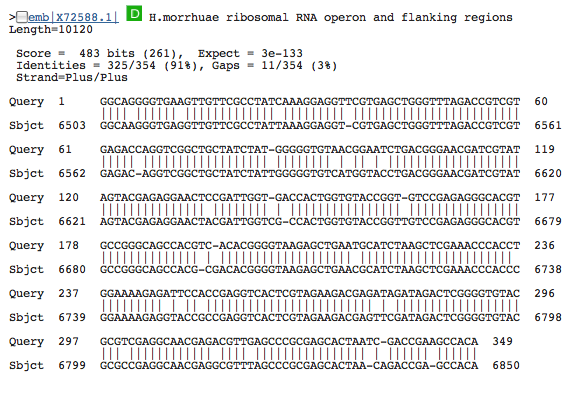
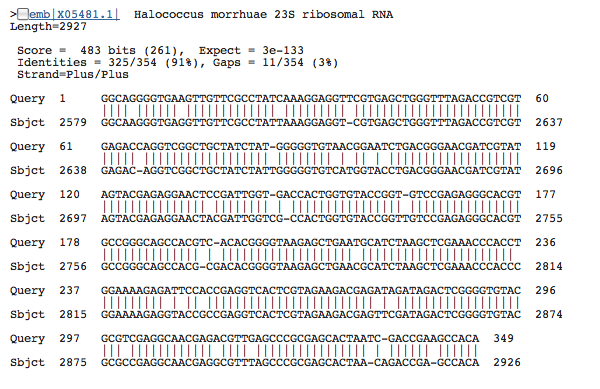
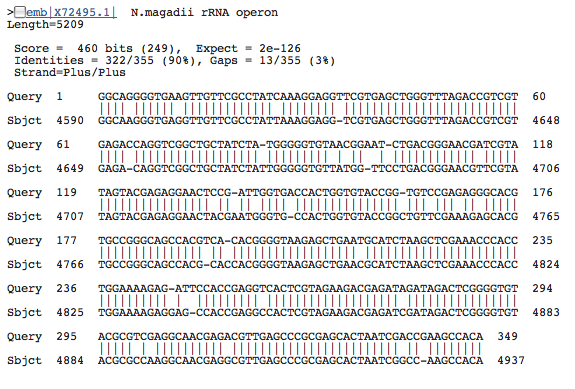
- 8 23S rRNA 644029745; 23S; 349bp: Top three genes with significant similarity:
- 9 Missing rRNAs
5s rRNA (445..583(+); 1766895..1767033(-); 1962..2100(+)), all three consisted of 139 identical base pairs.
The 5s rRNA is a component of the 50s ribosomal subunit in prokaryotes, and it often includes sites of inhibition for some antibiotics in some species.
16s rRNA (1770405..1771883(-); 1479bp): Top three species with similar 16s rRNA sequences
16s rRNA (3107428..3108907(+); 1480bp): Top three species with similar 16s rRNA sequences
16s rRNA (218960..219414(+); 455bp): Top three species with similar 16s rRNA sequences
23S rRNA
ID Number: 644033000
Location: (1..1863(+))
Length: 1863 bp
Top three genes with significant similarity according to BLAST:
23S rRNA
ID Number: 644032999
Location: (3109294..3111201(+))
Length: 1908bp
Top three genes with significant similarity according to BLAST:
23S rRNA
ID Number: 644031592
Location: 1767129..1770035 (-)
Length: 2907bp
Top three genes with significant similarity according to BLAST:
23S rRNA 644029745; 23S; 349bp: Top three genes with significant similarity:
This gene was, by far, the shortest 23S rRNA. 23s rRNA is usually a large molecule so this struck us as odd.
Missing rRNAs
We also wondered why our genome did not seem to contain 18S or 28S rRNA. 28S and 18S are normally found in eukaryotic genomes and we would not expect to find it in the species we are studying.